Are you wondering how to build an indoor positioning system (IPS)?
Indoor positioning technology is a valuable tool for both businesses and consumers. It has broad applications in retail, logistics, real estate, construction, public safety, and so much more.
In fact, according to a recent report, the global indoor location market was worth over $8.8 billion in 2022, and it is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 22.4% over the next five years to reach $24 billion by 2027. The adoption of technology in various verticals to enhance customer experiences is driving the demand for indoor location solutions.
But why exactly do businesses invest in indoor navigation technology?
GPS radio signals are not able to penetrate buildings composed of bricks, concrete, or metal. The typical accuracy of a GPS (5-10m) is not sufficient for indoor applications. And GPS signals indoors are too weak to be of any value. Indoor positioning systems are therefore required. For example, WiFi indoor positioning solutions use WiFi access points to detect transmitting WiFi devices, such as smartphones throughout indoor spaces.
In this article, you will learn how indoor positioning systems work in complex indoor environments and how to build a custom solution for your business. We’ll cover the basics of what it is, explore indoor positioning technologies, as well costs involved.
If you need to build an indoor map app, our team has the experience and resources to get the job done right. We’re happy to help you get started with a free consultation.
What is an indoor positioning system: definition, how does it work & common applications
An indoor positioning system helps locate people and objects indoors. It is used where GPS and other satellite technologies lack precision or fail entirely, such as inside multistory buildings, airports, parking garages, underground locations, etc.
To create an indoor navigation map, you’ll need to integrate an indoor positioning system. Traditional GPS systems, which rely on satellite signals, often fail to provide accurate positioning indoors due to obstructions like walls, ceilings, and floors. To overcome this limitation, IPS uses a variety of technologies, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth beacons, Ultra-wideband (UWB), and Radio Frequency Identification (RFID). The underlying technologies may differ drastically, but the majority of indoor positioning systems are beacon-based.
How does an indoor positioning system work?
An indoor positioning system provides geolocation data within indoor environments where traditional GPS might falter. Here’s how it functions:
- Signal source: IPS relies on signal sources like Wi-Fi routers, Bluetooth beacons, or UWB transmitters placed within the indoor space.
- Signal reception: Devices pick up these signals, with their strength, time, or angle indicating the device’s location.
- Position calculation: Algorithms process signal data to estimate the device’s position using techniques such as trilateration or triangulation.
- Display: The estimated position is shown on a digital map within an indoor navigation app.
- Data analysis: Modern IPSs also utilize data analytics, analyzing movement patterns for insights on user behavior or space management.
And what are indoor positioning system applications?
The applications of indoor positioning systems extend beyond just navigation; they include asset tracking, targeted marketing, security enhancement, and gathering data for analytics to improve user experiences and operational efficiency:
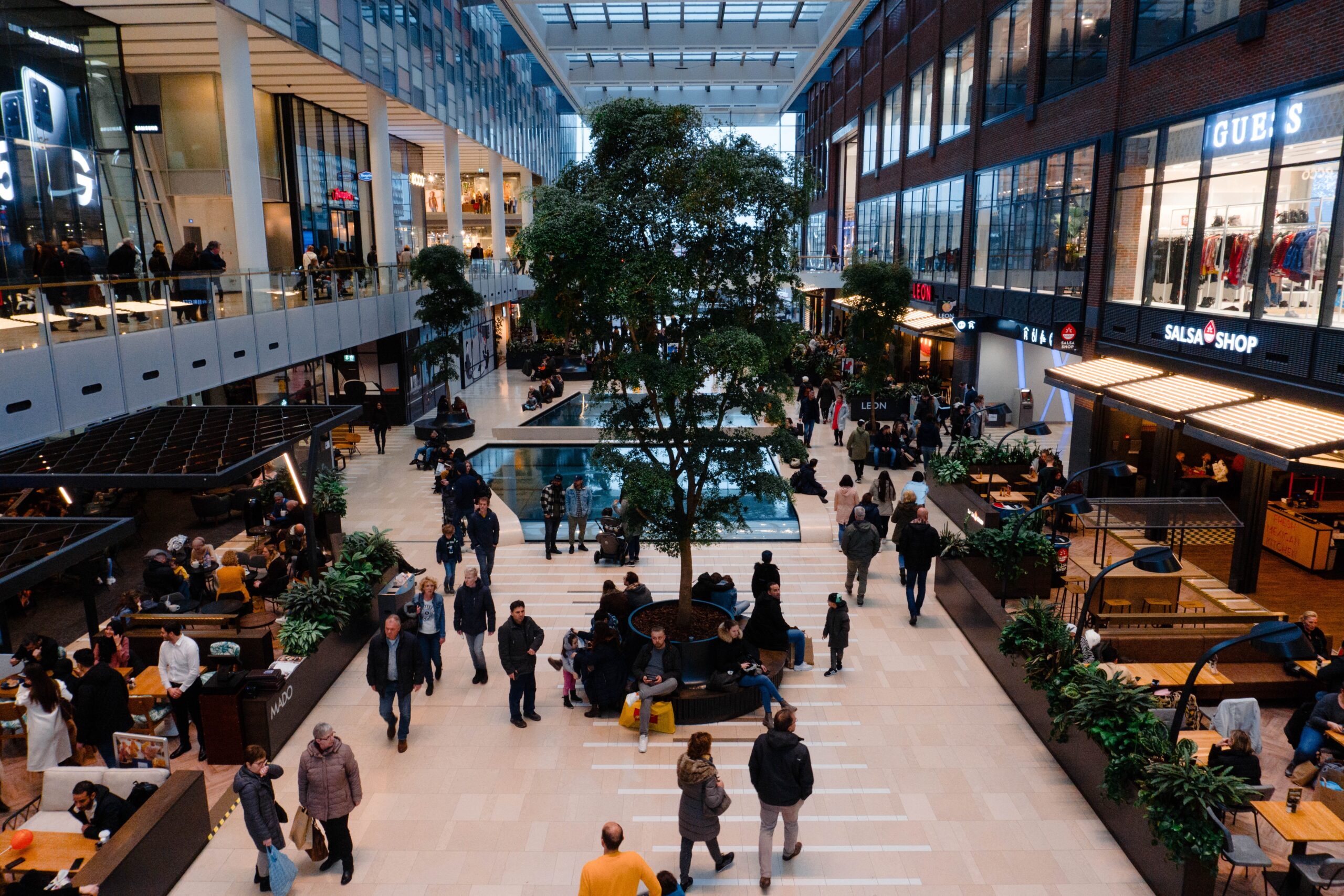
- Indoor navigation: Assisting visitors in navigating large facilities such as airports, shopping malls, and hospitals by providing real-time location-based guidance.
- Asset tracking: Monitoring the location and movement of assets within a facility, like equipment in hospitals or merchandise in retail stores.
- Targeted marketing: Offering promotions or advertisements to users based on their specific location within a venue, like a special deal when they’re near a particular store in a mall.
- Security and safety: Monitoring restricted areas or tracking the movement of personnel for security purposes. It can also assist in emergency evacuations by providing the quickest routes out.
- Data analytics: Gathering location-based data to analyze foot traffic patterns, optimize store layouts, or improve building design.
- Enhanced user experiences: Creating interactive museum tours, gaming experiences, or educational applications.
These are just a few examples, and the potential uses for IPS are vast, depending on the industry and specific needs of a business. If you have any questions about how you can use indoor positioning technology for your business, we would be happy to answer any questions you may have. Don’t hesitate to contact us via info@volpis.com
How to build an indoor positioning system: a step-by-step process
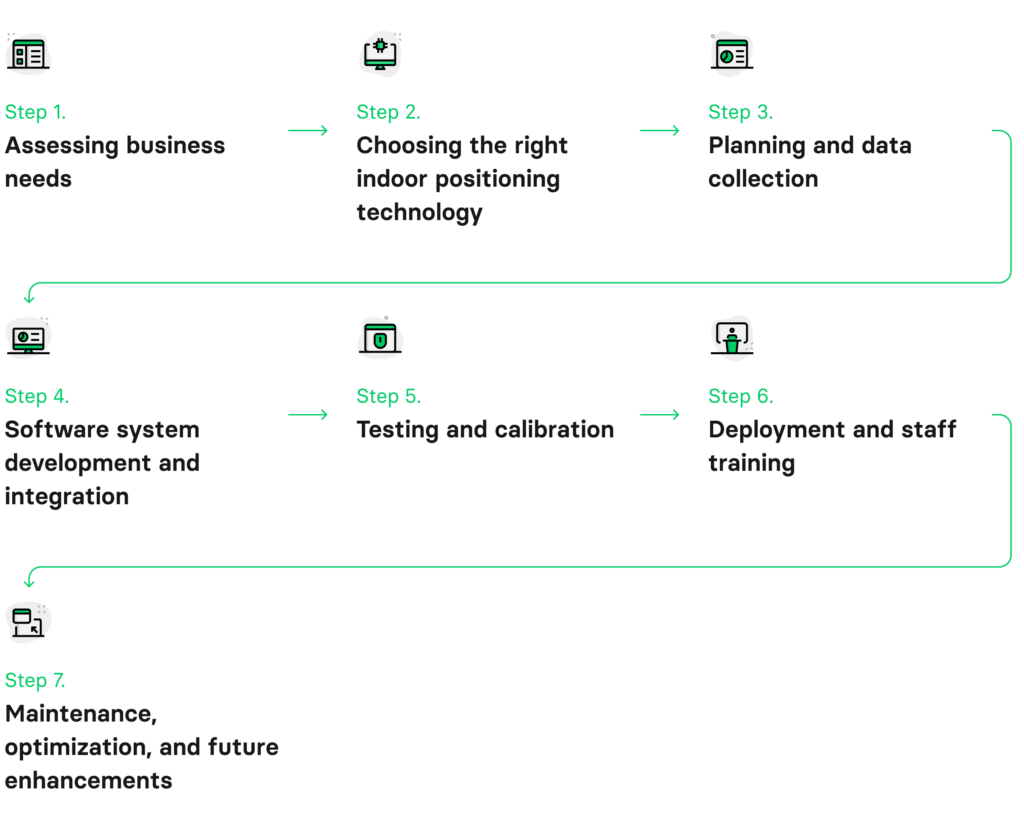
If you need to create indoor navigation maps, indoor positioning systems are essential tools that can provide accurate location data within buildings and complex structures. They are revolutionizing the way companies manage spaces, offering real-time location insights within structures where traditional GPS falls short. Let’s delve into the step-by-step process of building an IPS for your business.
Step 1: Assessing business needs
An indoor navigation system can have transformative effects on various businesses, addressing specific challenges and enhancing operations in each sector. Depending on your business type, the benefits of an IPS can vary considerably:
- For retailers, an indoor mapping solution can provide enhanced customer engagement and efficient inventory management.
- For healthcare facilities, an indoor navigation system offers enhanced patient navigation and the ability to track medical equipment accurately.
- Museums and cultural institutions benefit from heightened visitor interactions through interactive exhibits and the ability to efficiently manage crowds in popular areas.
- In smart buildings and offices, IPS fosters optimal workspace utilization and significantly boosts employee productivity.
- For logistics operations, IPS enables real-time tracking of assets, efficient order fulfillment, dynamic adjustments to warehouse layouts, and delivery route optimization. Also, it ensures accurate deliveries by guiding drivers to precise points, especially in complex areas.
Step 2: Choosing the right indoor positioning technology
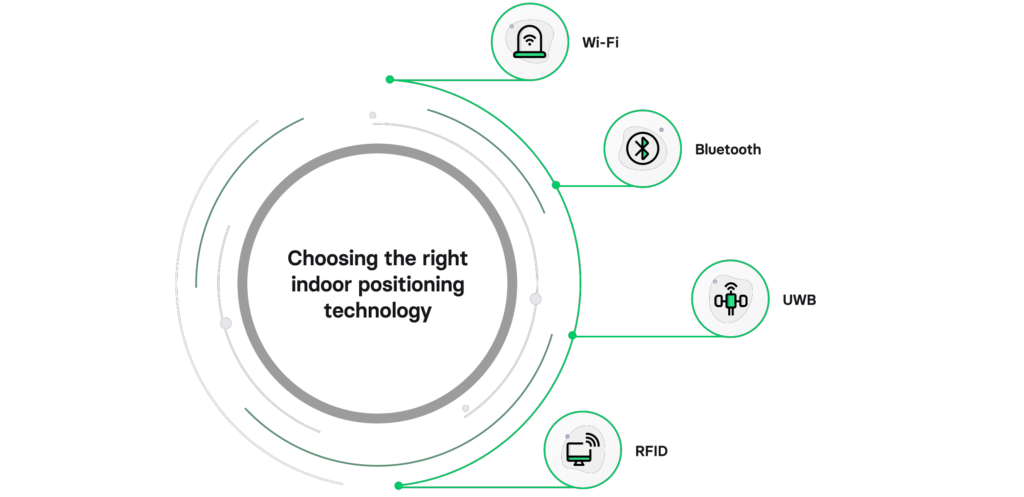
Selecting the appropriate indoor positioning technology is a crucial decision for businesses aiming to implement accurate and effective location-based solutions. Here’s a breakdown of the leading IPS technologies, their workings, and optimal application scenarios:
- Wi-Fi positioning uses the signals from Wi-Fi access points to determine the location of a device within a Wi-Fi network. Devices like smartphones scan for nearby Wi-Fi networks. By comparing the known locations of these Wi-Fi networks, the device’s location is estimated. It is commonly used in indoor navigation apps, retail spaces, and large public venues like airports and shopping malls.
- Bluetooth positioning (Bluetooth beacons) utilizes low-energy Bluetooth beacons placed in specific locations to communicate with nearby devices. When a device comes within range of a Bluetooth beacon, it receives signals and calculates its proximity to the beacon. By triangulating signals from multiple beacons, the device’s location is determined. Used for indoor navigation, location-based marketing, and context-aware applications in various environments, including retail stores and museums.
- Ultra-wideband (UWB) positioning uses short-range radio waves with a wide bandwidth to measure the time it takes for signals to travel between devices. UWB devices calculate distances between each other by measuring the time it takes for signals to travel. By combining these distance measurements, precise location information is obtained. It is ideal for applications requiring high accuracy, such as industrial automation, asset tracking, and indoor navigation in complex environments.
- Radiofrequency identification (RFID) uses radio waves to identify and track objects equipped with RFID tags, which contain unique information about the tagged item. RFID readers emit radio waves, which power up the RFID tags. The tags then respond with their unique information, allowing the reader to identify and track the tagged objects. It is widely used in supply chain management, inventory tracking, and asset management across various industries.
Each indoor positioning technique has its unique strengths, making it suitable for specific applications and environments. If you need to choose the most appropriate indoor positioning technology for your business objectives, don’t hesitate to contact us via info@volpis.com
Step 3: Planning and data collection
Creating an accurate floor plan and gathering precise location data are foundational steps in implementing an IPS. These steps ensure that the system operates efficiently, delivering accurate location information to users. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the process:
- Site survey and initial assessment: Undertake a comprehensive site survey to familiarize yourself with the layout/floor plan and determine key points of interest (such as security desk, vending machines, or meeting rooms).
- Laser measurements and surveying tools: Harness laser measurements and digital surveying tools to ensure precision in your floor plan and data-gathering process.
- Building Information Modeling (BIM): Utilize BIM technology to integrate and consolidate architectural plans, providing a cohesive view of the space.
- Wireless signal strength surveys: Conduct surveys to measure wireless signal strength, ensuring you’re aware of and can address any signal dead zones.
- Collecting location data: Implement GPS and beacon systems for data collection, further refined by techniques like fingerprinting and calibration for enhanced accuracy.
- Data analysis and preprocessing: Once data is collected, it’s essential to thoroughly analyze and preprocess it to ensure it’s optimized for IPS algorithms.
Step 4: Software system development and integration
Іndoor positioning systems are intricate technological solutions that rely heavily on software to function effectively. Software developers play a central role in the development, implementation, and continuous improvement of IPS. Here’s a breakdown of key actions that are needed for system development and integration:
- Algorithms development: Develop algorithms for trilateration, triangulation, and fingerprinting to accurately pinpoint indoor positions using signal patterns.
- Integration with hardware: Integrate sensors, such as accelerometers and gyroscopes, and sync with hardware like Bluetooth beacons or RFID readers.
- Database management: Design efficient databases for data storage and preprocess this data to eliminate inconsistencies, ensuring real-time precision.
- Mobile application development: Craft user-centric interfaces and integrate indoor positioning services for dynamic navigation experiences.
- ML and AI integration: Use machine learning for predictive user behavior analytics and employ AI for ongoing IPS accuracy improvements.
- Testing and debugging: Prioritize rigorous testing methodologies and incorporate user feedback to fine-tune the IPS.
- Security and privacy measures: Implement robust data encryption protocols and allow users granular control over their privacy settings within the IPS.
An effective IPS melds together precise algorithms, seamless hardware integration, user-friendly applications, and rigorous security measures. Attention to each of these facets ensures a reliable and efficient system.
Step 5: Testing and calibration
Testing and calibration is a critical phase in the implementation of an indoor positioning system. It ensures the system functions accurately, providing users with reliable indoor navigation experiences.
- Testing verifies the accuracy of the IPS, thoroughly evaluates the user interface, aids in pinpointing performance bottlenecks, and guarantees that data transmission is carried out securely and efficiently.
- Calibration fine-tunes the system, ensuring that the gathered data is precise and the positioning accuracy meets the desired standards. The calibration process involves adjusting sensors to ensure accurate readings and optimizing signal strength for reliable performance.
Step 6: Deployment and staff training
After finalizing the development and testing phases, integrating an indoor positioning system into your business operations is critical to get the system up and running effectively in its intended environment. Concurrently, comprehensive staff training ensures that your team is well-equipped to manage and assist users with the new indoor positioning system.
- During the IPS deployment process, it’s crucial to work closely with your development team. You’ll need to carry out an in-depth site assessment to determine the best locations for beacon installation, recognize potential barriers, and pinpoint zones with significant pedestrian movement.
- And by training your employees thoroughly on the intricacies of the IPS, you ensure that they are prepared to assist customers effectively. You can offer interactive training sessions that emphasize practical situations and typical customer questions.
Step 7: Maintenance, optimization, and future enhancements
Your indoor mapping solution will require continuous maintenance to ensure it functions optimally, delivering reliable indoor navigation experiences.
- By prioritizing ongoing maintenance, system optimization, and updates, businesses can ensure their indoor navigation system remains cutting-edge, reliable, and aligned with the evolving needs of users.
- By keeping an eye on emerging technological trends, such as AI-driven strategies and IoT integration, you can ensure that your IPS remains cutting-edge and offers an enriched experience to its users. Integrating these advancements can significantly enhance the functionality and user-friendliness of your indoor positioning system.
How to improve the accuracy of your IPS over time
The precision of an indoor positioning system is pivotal for ensuring optimal user experience and functionality. Business owners should prioritize enhancing this accuracy, as even minor discrepancies can significantly impact its overall effectiveness.
1. Continuous monitoring of system performance
Consistent supervision of your IPS can reveal crucial insights and areas for improvement.
- Real-time monitoring: Implement real-time monitoring tools to track system performance, including location accuracy, response times, and signal strength. Regularly analyze this data to identify any deviations from the desired benchmarks.
- User feedback analysis: Actively gather and analyze user feedback. Understand common issues reported by users and use this information to address pain points promptly.
2. Troubleshooting common issues
A proactive approach to identifying and resolving issues ensures a smoother user experience.
- Identify patterns: Monitor for recurring issues or patterns reported by users. If multiple users face similar problems, investigate and resolve the root cause to enhance the overall user experience.
- Prompt support: Offer prompt customer support to assist users facing issues. Maintain a dedicated support team that can address problems in real time, ensuring customer satisfaction.
3. Implementing software upgrades
Keeping software updated is key to ensuring an IPS’s efficiency and user satisfaction.
- Regular software updates: Release regular software updates with bug fixes, security enhancements, and new features. Encourage users to keep their mobile apps updated to benefit from the latest improvements.
- User-friendly update process: Ensure that updating the IPS software is a seamless process for end-users. Provide clear instructions and notifications within the app, guiding users on how to update without any hassle.
4. System optimization
Optimizing the system holistically ensures that it remains agile and adaptive to changing user needs.
- Data analysis: Continuously analyze system data to identify trends, usage patterns, and areas for optimization. Optimize algorithms, data processing, and server configurations based on these analyses.
- Battery optimization: Optimize the IPS to minimize battery consumption on users’ devices. Efficient use of sensors and wireless communication technologies helps extend battery life.
5. Integrating technological advancements
Staying updated with technological advancements can significantly boost the IPS’s performance.
- AI-driven enhancements: Explore AI-driven enhancements such as machine learning algorithms that continuously improve IPS accuracy based on user behavior and feedback.
- IoT integration: Integrate IPS with Internet of Things (IoT) devices. For instance, connect IPS with smart lighting systems that adjust illumination based on user presence, enhancing energy efficiency and user experience simultaneously.
6. Security and privacy measures
Prioritizing security and privacy ensures trust and promotes broader adoption of your IPS.
- Regular security audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities. Implement robust encryption, secure communication protocols, and access controls to safeguard user data.
- User privacy: Clearly communicate data usage policies, provide opt-in mechanisms for location services, and allow users to control their locational information.
How to use indoor positioning system to enhance customer experience
An indoor positioning system offers businesses a powerful tool to enhance customer engagement within indoor spaces. By leveraging IPS technology, businesses can provide personalized services, collect data, streamline navigation, and deliver targeted promotions. Here are the main ways businesses utilize indoor navigation maps to enrich customer interactions:
Contextual messaging
Utilize IPS to send personalized notifications to customers’ smartphones based on their real-time location within your premises. For instance, welcome messages near entrances or special offers near specific product displays.
Event and promotion alerts
Send notifications about ongoing events, sales, or promotions to customers as they approach relevant areas. Tailoring messages based on location ensures they are timely and relevant.
Interactive maps
Integrate indoor maps into mobile apps, allowing customers to easily find products, departments, or amenities. Implement turn-by-turn navigation to guide them to their desired destinations efficiently.
Accessible routes
Offer accessible routes for individuals with disabilities, ensuring inclusivity in navigation assistance.
Proximity marketing
Trigger location-based promotions or discounts when customers are near specific products or sections of the store. For example, offer a discount on accessories when customers are near the electronics section.
Interactive exhibits
Museums and art galleries can utilize IPS to create interactive exhibits triggered by visitors’ proximity. Visitors can receive detailed information about artworks as they approach, enhancing their understanding and engagement.
Use cases of indoor positioning systems: examples of businesses effectively utilizing indoor navigation
Businesses across various sectors are capitalizing on indoor navigation to map large buildings and help customers navigate through their venues. Let’s explore real-world examples of industries harnessing indoor navigation to its fullest potential.
Retail stores
Retail giants like Walmart and Target use IPS to guide customers to specific products, offer personalized discounts, and notify them about ongoing promotions, significantly enhancing the shopping experience.
Airports
Airports like Amsterdam Airport Schiphol employ indoor mapping solutions to guide passengers to gates, services, and amenities, reducing the stress associated with navigating large terminals.
Shopping malls
Shopping centers like Westfield London use IPS to offer personalized shopping recommendations, provide indoor maps for easy navigation, and send notifications about sales and events to visitors’ smartphones.
Hospitals
Hospitals such as Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles utilize IPS to guide patients and visitors to specific departments, doctors’ offices, and facilities within the hospital, improving overall patient experience.
Museums
Museums like the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington, D.C., use IPS to provide interactive exhibits, delivering detailed information about exhibits as visitors approach, creating a more engaging museum experience.
How much does an indoor positioning system cost?
Systems leveraging Bluetooth beacons start from around $20,000 to $30,000. However, the overall cost of the indoor mapping solution can escalate depending on the technology chosen, the size of the area that needs coverage, the complexity of the software, and the hardware requirements.
Additionally, ongoing maintenance, software updates, and potential infrastructure modifications can influence the overall cost of your indoor navigation app.
Our team has an impressive track record with a long history of successfully completed projects, and we would be happy to provide you with an estimate. Please don’t hesitate to contact us via info@volpis.com
Our experience in building custom indoor positioning systems
Our team has extensive experience in indoor navigation app development. Regularly ranked among the Top Custom Software Development Companies on Clutch, Volpis has been leveraging the power of technology to assist business owners in reaching unparalleled milestones.
To build custom indoor mapping solutions, we take into consideration the specific features of your building, as well as your specific business processes. Volpis can help you with:
- Project planning and requirements gathering
- Designing the indoor navigation map
- Creating indoor maps from scratch
- Upgrading existing systems
- Leveraging IoT location-based service technologies
- Addressing security concerns
- Customizing the system to fit your needs
We have been working in this field for years and have seen it all. Our experts can provide detailed recommendations, so you can get the solution that works best for your needs. An indoor positioning system can be a great way to improve productivity, safety, and overall efficiency. By using an IPS you can optimize your space to make sure that it is being used as effectively as possible.
If you plan to create an indoor navigation map and would like to learn more about our services, please contact us for more information. We’ll work with you to develop a plan that is tailored to your company’s needs and budget.
Do you plan to build an indoor positioning system?
Indoor positioning systems are a key component of any indoor location solution. They help to ensure that you have accurate information about the location and movement of people within your building.
In order to properly implement an indoor positioning solution, you must first understand the requirements for your system and the expected results. Next, you must determine how to best achieve those results. Finally, you need to test your system in the real world and make any adjustments necessary to improve its performance.
If you have questions about indoor positioning systems or plan to develop your own indoor mapping platform, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us via info@volpis.com
Frequently asked questions
Indoor navigation refers to guiding users or assets within an enclosed space using digital tools, maps, and signals, where traditional GPS isn’t effective. It provides real-time location-based services, allowing for route planning, asset tracking, or location-based interactions within buildings or structures. The technology is similar to outdoor GPS but is adapted for indoor complexities. To create indoor navigation maps, one typically starts with a detailed floor layout of the building and then overlays digital markers and pathways to guide users efficiently. These maps can be accessed via mobile devices, offering users an experience similar to what they’re accustomed to with platforms like Google Maps, but tailored to the intricacies of an indoor environment. Integrating such maps with the familiar interface of apps on the mobile device ensures user-friendly navigation.
Indoor positioning systems come in various forms, including Wi-Fi positioning, Bluetooth beacons, Ultra-wideband (UWB), and Radio Frequency Identification (RFID). Each system has its unique strengths and optimal application scenarios. The choice of system often depends on factors like accuracy requirements, infrastructure, and the intended application. For example, beacons map can translate received radio signals into precise data, enabling users to find all the shops within a mall or navigate large venues. These systems can determine locations with 0/1–3 meters accuracy, based on the physical properties of the signals. By integrating this data with real-world coordinates, businesses can offer a seamless navigation experience that reflects the physical layout of their space.
The time it takes to build a custom indoor positioning system depends on the project’s needs. The larger the project and the more complex or unique the features are, the longer it will take to create custom indoor navigation maps. For developers who have limited experience in this field, it will take more time than for a team that has designed such systems before. When developing an indoor navigation map, it’s vital to ensure that accurate maps provide clarity for users, especially when accessed on a mobile device. Many businesses prefer to design their own indoor maps to cater to their specific requirements, making the search for the best indoor mapping solution crucial. The nuances of indoor map design can further influence the duration of the project.
Traditional GPS struggles indoors due to obstructions like walls and ceilings that block satellite signals. However, assisted GPS (A-GPS) can use nearby Wi-Fi networks or cellular towers to provide rough indoor positioning. For precise indoor tracking, dedicated indoor positioning systems are generally preferred.
UWB (Ultra-wideband) is often touted as one of the most accurate indoor positioning technologies, offering location precision down to a few centimeters. However, the “best” system can vary based on specific requirements, infrastructure, and budget. It’s essential to consider the application’s needs when selecting an IPS.
Indoor positioning analytics refers to the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data generated by indoor positioning systems. This can include tracking foot traffic patterns, understanding dwell times in specific zones, or gauging asset utilization in a facility. By analyzing this data, businesses can make informed decisions to improve operations or enhance user experiences.
Several companies are pioneers in indoor navigation, including Apple with its Indoor Mapping Data Format (IMDF), Google with its Indoor Maps, and HERE Technologies. Others like IndoorAtlas and Estimote offer specialized solutions for various sectors. The competitive landscape is rapidly evolving, with many players offering innovative solutions.
The indoor positioning & navigation system market has seen significant growth over recent years due to increasing applications in retail, healthcare, and manufacturing sectors. Estimates suggest it’s a multi-billion dollar market, and its value is expected to rise with the proliferation of IoT and smart building technologies. Factors like improved customer experience and operational efficiency drive the demand.

Kostya Khuta, the CEO of Volpis, is an expert in crafting custom software solutions for the Fleet Management, Logistics, and Transportation industry. With over 8 years of experience, he leads the way in delivering innovative and tailored solutions to meet industry-specific needs.