Choosing between Flutter vs native app development in 2026? You’re not alone.
Whether you’re a startup founder building your MVP or a product manager scaling an existing product, this decision directly impacts your app’s performance, cost, and long-term maintainability.
Both approaches are powerful, but serve different goals:
- Flutter is ideal when speed, cross-platform consistency, and cost-efficiency matter most.
- Native development excels when top-tier performance, deep hardware access, or platform-specific design precision is critical.
Flutter is a popular open-source framework that lets developers build apps for mobile, web, and desktop from a single codebase. Created by Google, Flutter has gained a large following among developers. With Flutter, you write your app once, and it works on all devices. It’s like making three for the price of one.
On the other hand, native development involves creating apps tailored for specific platforms like iOS, Android, or Windows. For example, if you’re making an app for iOS, you’ll need a Mac and you’ll probably be using Swift or Objective-C with Xcode. But if you’re building for Android, you’re likely to be coding in Java or Kotlin with Android Studio.
From MVPs and internal tools to high-performance apps with AR or third-party device integrations, we’ll walk through real-world use cases and help you decide what fits your project.
We’ll also cover key differences in performance, UI behavior, cost-efficiency, and long-term scalability, including trade-offs like Flutter vs native Android and Flutter vs native iOS.
Consistently recognized as one of the top software development companies on Clutch, Volpis has designed and developed 50+ apps using both Flutter and native stacks. We’ve seen when each one works best — and where it fails. If you have any questions about Flutter or native app development, we would be happy to answer all your questions and give honest advice. You can always reach out to us via info@volpis.com
That’s why we created this guide: to help you make a data-driven, experience-backed decision.
Flutter vs native comparison for 2026

Both Flutter and native development allow building robust features and have earned their place in the development world.
| Flutter development | Native development | |
| Cost | Using Flutter for development saves costs because it works on multiple platforms. Additionally, Flutter’s rapid development cycles and code reusability allow businesses to deploy updates and features faster, thereby lowering labor costs and time-to-market. It’s important to note that while Flutter speeds up the development process, it’s not always twice as fast as native development. There are still platform-specific adjustments and integrations that need to be made. But overall, Flutter can accelerate the development process by about 1.5 times compared to native development, making it a highly efficient choice for many projects. | Using native technologies involves higher costs due to the need for specialized teams proficient in platform-specific languages like Java/Kotlin for Android or Objective-C/Swift for iOS. Maintaining separate codebases for each platform also increases long-term maintenance expenses, as updates and bug fixes must be implemented individually. |
| Performance | Flutter achieves high performance by compiling code into native ARM code, which runs efficiently on devices. However, because Flutter adds an abstraction layer between its code and the native platform, there can be minor differences in performance compared to fully native apps that directly access device features. | Native apps are optimized for specific platforms like Android or iOS, ensuring they leverage the platform’s capabilities fully, which often results in slightly better performance than cross-platform solutions. |
| User interface | Flutter provides a rich set of widgets for building user interfaces, promoting consistency across different platforms. Yet, achieving pixel-perfect designs across various screen sizes and resolutions can be more challenging with Flutter compared to native development. | Native development utilizes platform-specific UI controls and adheres closely to each platform’s design guidelines (such as Material Design for Android and Human Interface Guidelines for iOS), ensuring UI elements look and function seamlessly on each device. |
| Development environment | Flutter’s single codebase for Android and iOS applications accelerates development cycles. This approach allows developers to write once and deploy on multiple platforms, reducing development time and effort significantly. | If you go the native route, you have to build separate versions for Android and iOS, using different languages (like Java/Kotlin for Android, Swift/Objective-C for iOS) and tools (Android Studio for Android, Xcode for iOS). That can take longer because you’re essentially building two different apps. |
| IDE and operating system support | Flutter developers can use Android Studio or Visual Studio Code on Windows, Mac, or Linux—whatever floats your boat. So you can work where you’re most comfortable. | Android developers typically use Android Studio or other tools like Eclipse or IntelliJ on Windows or Mac. iOS developers are more limited—they’ve gotta use Xcode, and that’s only available on Macs. |
| Community | The Flutter community is growing fast and they’re constantly adding new stuff like cool widgets and helpful plugins. This means you’re not alone when you’re building Flutter apps; there’s a whole gang out there to help you out. | Native platforms like Java for Android and Objective-C for iOS have been around forever and have big communities with tons of resources and advice built up over time. |
Flutter vs native development: advantages & disadvantages

When it comes to choosing between Flutter and native development, understanding their capabilities and limitations can make a big difference. Let’s dive into what each offers.
Flutter development advantages and disadvantages
Flutter enables building apps across multiple platforms from a single codebase. However, it comes with its own set of challenges.
| Flutter development advantages | Flutter development disadvantages |
| Flutter makes waves with its ability to create apps across multiple platforms like Android, iOS, Web, and even Cloud applications using a single codebase. This not only streamlines development but also ensures consistency across different platforms. One of the standout features of Flutter is its Hot-Reload capability. Unlike traditional native development where developers often have to wait to see small changes, Flutter allows instant testing of code modifications. This speeds up the development process significantly. From a financial standpoint, Flutter can be a game-changer. By enabling developers to build for both Android and iOS from a single codebase, it reduces overall project costs. This cost-effectiveness is a major reason why many are shifting from native development to Flutter. | While Flutter performs well for most applications, it may not be the best choice for performance-intensive tasks like complex animations, high-performance gaming, or apps requiring extensive computational operations. Flutter may have limitations in accessing platform-specific features and APIs, especially when compared to native development. For example, advanced features like ARKit (iOS), HealthKit (iOS), or custom Bluetooth operations might require more effort to implement. Flutter apps tend to have a larger binary size compared to native apps. This is due to the inclusion of the Flutter engine and the necessary libraries, which can be a drawback for users with limited storage space. While Flutter’s ecosystem is growing, it is still relatively new compared to native development ecosystems like those for iOS and Android. This can result in fewer available third-party libraries and plugins, or sometimes less mature ones, which might not cover all needs or be as reliable as their native counterparts. Although Flutter provides a consistent UI across platforms, it might not always align perfectly with the native look and feel of iOS and Android. For applications that require a very native user experience that strictly follows platform-specific design guidelines, native development might be preferred. |
Native development advantages and disadvantages

Native development excels in delivering optimized performance tailored to each platform, ensuring seamless integration with hardware and native user experiences. Yet, the approach requires separate development efforts for Android and iOS, potentially increasing costs and development time.
| Native development advantages | Native development disadvantages |
| When it comes to performance optimization, native development shines. Apps are finely tuned for each platform, ensuring optimal performance, which is crucial for resource-intensive applications. Native applications also boast a genuine native look and feel. They seamlessly integrate with the platform’s design standards, offering users a familiar and intuitive experience that can be hard to replicate with cross platform solutions like Flutter. Hardware integration is another area where native development excels. There’s no additional layer between the app and the device’s hardware, leading to seamless integration and efficient use of device capabilities. Furthermore, native languages like Java (for Android) and Swift (for iOS) have extensive libraries and plugins available. This robust ecosystem accelerates development by providing pre-built solutions, thereby reducing project duration. | Development with native technologies does come with its challenges. One notable drawback is higher development costs. Since separate code bases and teams with knowledge of different programming languages are required for Android and iOS development, this can lead to increased project expenses. |
Flutter vs native performance (2026 expert breakdown)

Performance is one of the most decisive factors when choosing between Flutter vs native app development, especially for products involving animation-heavy interfaces, real-time features, or deep hardware access.
While Flutter has come a long way and performs well for most general-purpose apps, native development still offers unmatched control, lower-level optimization, and better access to platform-specific features. This can make a major difference in apps where milliseconds matter.
Let’s break it down platform by platform.
Flutter vs native Android performance

Flutter compiles Dart code to native ARM binaries and uses its own Skia rendering engine to draw every pixel on the screen. While this approach ensures design consistency across platforms, it also introduces an additional layer of abstraction between the app and the Android operating system.
In contrast, native Android apps built with Kotlin or Java have direct access to the Android SDK, rendering pipeline, and background services. This enables tighter system integration and lower overhead.
| Performance Factor | Flutter (Android) | Native Android (Kotlin/Java) |
| Startup time | Slightly slower due to bundled engine | Faster cold & warm starts, optimized by ART |
| Rendering | Uses Skia; custom widgets mimic native look | Uses native Material components rendered by Android’s UI system |
| Animations (FPS stability) | Stable under light load; may drop frames during stress | Highly optimized with GPU acceleration, SurfaceView, RenderThread |
| Background execution | Requires plugins for WorkManager, foreground services | Deep system integration (JobScheduler, Services, AlarmManager) |
| Battery efficiency | Acceptable but may consume more during heavy UI tasks | More optimized due to lifecycle-aware components and platform controls |
| Multithreading | Limited via Isolates | Full control with Coroutines, Executors, and concurrency primitives |
| Sensor access | Plugin-based; less flexibility | Direct access via SensorManager, NDK, CameraX |
| Advanced hardware features | Requires manual channel bridging | Native access to ARCore, LiDAR (via Depth API), NFC, BLE, USB, IoT devices |
| App size (APK) | Typically +2–6MB larger than native | Smaller footprint, modularized with R8 and dynamic delivery |
Expert insight: Flutter is ideal for Android apps with standard interfaces and logic — like dashboards, admin panels, and customer portals. But if you’re building apps with camera integration, background syncing, real-time GPS tracking, AR overlays, LiDAR, BLE sensors, USB/serial IoT devices, or advanced animations, native Android gives you more control, stability, and performance headroom.
Flutter vs native iOS performance

On iOS, Flutter performs well in many cases — compiling to native ARM code and using its Skia engine to render UI. But unlike native iOS apps, Flutter doesn’t use UIKit or SwiftUI. This makes its rendering feel slightly different and can create friction in scenarios requiring pixel-perfect native behavior or access to newer Apple features.
Meanwhile, native iOS apps built with Swift or Objective-C benefit from tight OS integration, direct access to Apple’s frameworks, and optimization baked into the iOS runtime.
| Performance factor | Flutter (iOS) | Native iOS (Swift/Objective-C) |
| Startup time | Slightly delayed due to engine initialization | Lightning-fast, tightly optimized by iOS |
| Rendering | Skia engine replicates UI | Native rendering via UIKit or SwiftUI |
| Animations & gestures | Smooth, but can exhibit latency under stress | Ultra-responsive with Core Animation and Metal |
| Advanced UI support | Custom implementation required for Apple’s newer patterns | Direct use of SwiftUI, SF Symbols, haptics, blur effects, etc. |
| System APIs | Requires plugins or channels | Seamless access to ARKit, CoreML, HealthKit, HomeKit, FaceID, etc. |
| Multitasking & background | Limited background modes | Full support for Background Fetch, PushKit, CoreMotion, Background Audio |
| Sensor & hardware access | Indirect; may lag behind SDK updates | Native access to camera, gyroscope, accelerometer, secure enclave |
| Battery efficiency | Reasonable, but less optimized | Fully managed by Apple frameworks, better thermal handling |
| App size (.IPA) | Typically 20–40% larger | Smaller, thinned via Bitcode and App Store delivery |
Expert insight: For apps focused on iOS, especially those needing ARKit, LiDAR, motion sensors, FaceID, or tight compliance with Human Interface Guidelines, native iOS development is the clear winner. Flutter can handle basic UIs and logic well, but the more Apple-specific your app becomes, the harder it is to keep the experience truly native without custom plugins and compromises.
What Flutter still struggles with (both platforms)
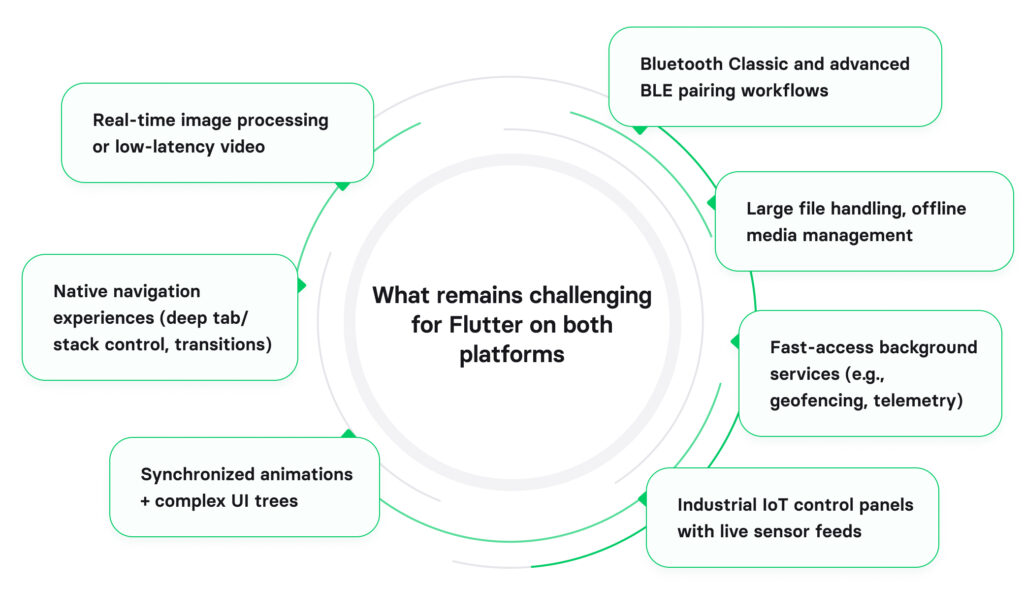
While Flutter excels in cross-platform development, there are still certain use cases where it faces performance or integration challenges on both Android and iOS:
- Real-time image processing or low-latency video
- Bluetooth Classic and advanced BLE pairing workflows
- Native navigation experiences (deep tab/stack control, transitions)
- Large file handling, offline media management
- Synchronized animations + complex UI trees
- Fast-access background services (e.g., geofencing, telemetry)
- Industrial IoT control panels with live sensor feeds
When to choose each: use cases of native and Flutter development
When deciding between Flutter and native, there are a lot of factors to consider. Let’s dive into some common scenarios to help you figure out which platform is right for your project.
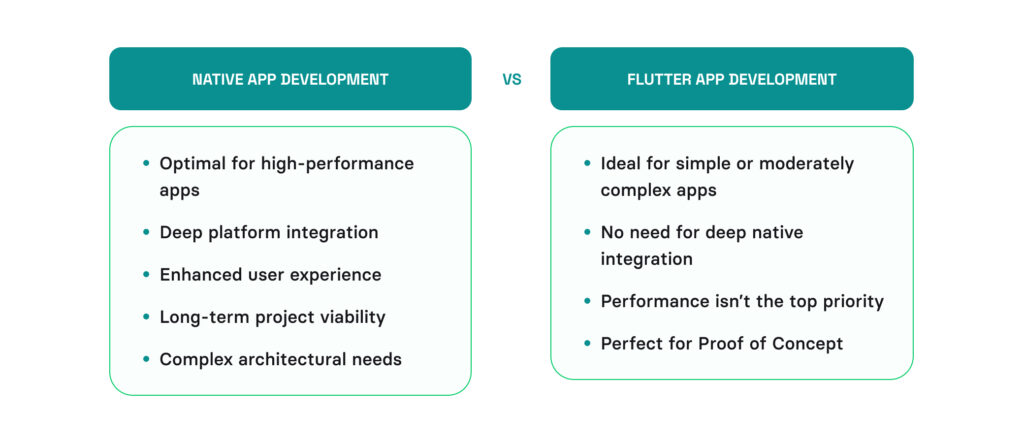
When to go for native app development:
- Optimal for high-performance apps: Native development is preferable for applications requiring maximum performance, such as those with intensive graphics or complex animations.
- Deep platform integration: When your app needs to leverage specific platform features like ARKit, HealthKit, device sensors, or custom Bluetooth operations, native development provides better support and integration.
- Enhanced user experience: Native development enables adherence to platform-specific design guidelines, providing a more intuitive and responsive user experience.
- Long-term project viability: For projects expected to evolve over a long period, native development offers better alignment with platform updates and optimizations.
- Complex architectural needs: If your app has sophisticated architectural requirements, native development offers more flexibility and control to meet these needs.
When to go for Flutter app development:
- Ideal for simple or moderately complex apps: If your project involves a relatively simple application with straightforward features, Flutter is a fantastic choice. Flutter’s single codebase allows for faster development, which is perfect for apps that don’t need to push the hardware to its limits.
- No need for deep native integration: When your app doesn’t require integration with native features like ARKit, HealthKit, or custom device sensors, Flutter provides a more efficient development process. This cross-platform framework abstracts away much of the complexity, allowing you to focus on building your app rather than dealing with platform-specific intricacies.
- Performance isn’t the top priority: For apps where performance is important but not critical, Flutter offers a balance between speed and efficiency. While native development might squeeze out every last bit of performance, Flutter delivers an experience that’s more than sufficient for most use cases.
- Perfect for Proof of Concept (PoC): If you’re looking to develop a Proof of Concept or an MVP, Flutter is ideal. Its rapid development cycle and cross-platform nature allow you to quickly create and iterate on your app, helping you validate your idea without committing extensive resources.
Volpis advice: Flutter or native?

From years of experience, we would suggest the following:
- Choose native if your app demands maximum performance, deep platform integration, or long-term scalability. It’s the gold standard for apps involving AR, sensors, real-time data, offline sync, or mission-critical logic — especially in industries like mobility, logistics, healthcare, or fintech.
- Choose Flutter if you need to move fast, validate an idea, or build an app that doesn’t rely heavily on native APIs. It’s ideal for MVPs, internal tools, or cross-platform apps with moderate complexity where speed and UI consistency are the main goals.
Both approaches have proven success in the real world. The right choice depends not only on tech specs, but on your product vision, team capabilities, and time-to-market needs.
2026 update: what about Kotlin Multiplatform?

In the past year, we’ve successfully delivered several apps using Kotlin Multiplatform (KMP) — and for the right project, it’s become a serious contender.
Unlike Flutter, KMP allows teams to share business logic while preserving native UI or even share UI with Compose Multiplatform. This means you get the benefits of cross-platform development without compromising on platform fidelity or performance.
At Volpis, we recommend KMP when:
- Native UI matters, but code reuse is still a priority
- You’re already invested in Kotlin
- The product requires long-term scalability, especially across Android and iOS
In short, if you’re weighing Flutter vs native, it may be worth asking:
“Would Kotlin Multiplatform give us the best balance of performance, architecture, and maintainability?”
Popular apps built with Flutter
While native development remains the gold standard for performance, system integration, and long-term scalability, Flutter has proven itself capable of supporting large-scale, production-ready apps, particularly for businesses prioritizing cross-platform consistency and faster time to market. Below are well-known apps that are built with Flutter.
Reflectly
One of the most downloaded journaling and self-care apps in the world, Reflectly was built entirely with Flutter. Its beautiful UI and smooth animations showcase Flutter’s strength in delivering polished, user-centric interfaces, especially in lifestyle and wellness categories.
Alibaba
While the main app uses native code, parts of the Alibaba app—especially modules used internally and in sub-products—leverage Flutter for faster delivery across Android and iOS.
My BMW

BMW transitioned the entire codebase of their mobile app to Flutter, enabling feature parity and consistent UI across iOS and Android platforms. As of 2023, the My BMW app is fully powered by Flutter and available in over 40 countries — a rare case of Flutter being used in a mission-critical automotive application.
eBay Motors

This app was rebuilt with Flutter to enhance development speed and maintain consistent performance and design across platforms. Flutter excels at building cross-platform apps without compromising design or core functionality.
How Volpis can bring your app vision to life
Consistently recognized as one of the top custom software development companies on Clutch, our team at Volpis has rich experience designing and developing applications with both Flutter and native technologies. Our team, consisting of over 40 in-house experts, brings extensive experience and creativity to each project.
Our commitment to excellence is reflected in the glowing reviews from our customers, who consistently praise our dedication to delivering exceptional results.

Read more reviews from our valuable customers here
We invite you to explore our portfolio for a detailed look at the innovative software systems we have developed for our clients. Whether you need a cross-platform solution with Flutter or a platform-specific app with native development, we’ve got the expertise to bring your vision to life.
We’d love to answer any questions you may have about Flutter and native app development. You can reach out to us via info@volpis.com with any questions or to explore how we can be part of your journey.
Questions & Answers
FAQ
Is Flutter future-proof for cross-platform mobile development?
Flutter is designed to be future-proof in cross-platform app development, leveraging the Dart programming language for efficient app development across Android and iOS. This framework compiles code to native ARM code, ensuring performance comparable to native apps on both platforms. Dart’s strong typing system and ahead-of-time (AOT) compilation contribute to Flutter’s robustness in handling future updates and advancements in mobile technology. Businesses adopting Flutter can benefit from its scalability and adaptability, accommodating evolving industry standards and technological advancements over time.
How do native technologies enhance platform-specific apps?
Native development, using languages like Kotlin for Android and Swift for iOS, optimizes apps to fully leverage each platform’s unique features. This approach ensures seamless integration of platform-specific functionalities such as BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) and hardware sensor access, crucial for applications requiring high performance and precise device interactions. Native mobile apps are directly compiled into the device’s machine code, maximizing efficiency and responsiveness, which is particularly beneficial for resource-intensive domains like e-commerce and medical applications. Leveraging native technologies empowers developers to harness platform-specific advantages, enhancing app performance and user experience across diverse mobile ecosystems.
What are the advantages of Flutter over other cross-platform frameworks?
Flutter stands out among cross-platform frameworks due to its one codebase approach and Hot Reload feature, which allows developers to instantly view changes made to the code. This accelerates the development cycle and reduces time-to-market for mobile apps, enhancing productivity and agility in app development. Dart’s Just-in-Time (JIT) compilation further supports rapid iteration, making Flutter a preferred choice for mobile developers seeking to streamline their development process while maintaining high-quality performance. Flutter’s extensive widget library and customizable UI components facilitate the creation of visually appealing and responsive apps that meet the design guidelines of both Android’s Material Design and iOS’s Human Interface Guidelines.
How does Flutter simplify the development of Android and iOS apps?
By enabling developers to write one codebase for both iOS and Android development, Flutter minimizes the complexity associated with maintaining separate codebases. This unified approach not only reduces mobile development time but also lowers costs, as businesses can allocate resources more efficiently across mobile platforms. Flutter’s comprehensive widget library and customizable UI components facilitate the creation of apps that meet the design guidelines of both Android’s Material Design and iOS’s Human Interface Guidelines. Developers benefit from Flutter’s cross-platform capabilities, which streamline app deployment and maintenance.
What are the challenges of achieving pixel-perfect designs with Flutter?
While Flutter provides a rich set of widgets for building consistent UI across platforms, achieving pixel-perfect designs across various screen sizes and resolutions can require meticulous customization. Designers and developers may need to fine-tune layouts, typography, and animations to ensure visual coherence and usability on different devices. Despite these challenges, Flutter’s flexibility and extensive community support offer resources and best practices to help mobile developers achieve high-quality design fidelity in their apps. Flutter’s cross-platform technologies empower developers to create visually appealing and responsive apps that meet the design standards of both Android’s Material Design and iOS’s Human Interface Guidelines.
How does native development ensure a quality user experience on Android and iOS?
Natively compiled applications are developed using platform-specific SDKs and tools, ensuring adherence to Android’s Material Design principles and iOS’s Human Interface Guidelines. This approach guarantees that UI elements and interactions align with user expectations on each platform, enhancing usability and user satisfaction. Native development also leverages advanced features and optimizations tailored to Android and iOS ecosystems, such as efficient memory management and native API access, which contribute to smoother performance and responsiveness. Developers benefit from native development’s comprehensive ecosystem and platform-specific optimizations, ensuring quality user experience across diverse mobile environments.
What are the advantages of using native languages for mobile app development?
Native languages like Kotlin for Android and Swift for iOS offer several advantages in mobile app development, including access to platform-specific APIs and libraries. Developers proficient in these languages can leverage extensive documentation and community support to implement complex features and functionalities efficiently. Kotlin’s interoperability with Java and Swift’s safety features further enhance developer productivity and code quality, making native mobile development a preferred choice for applications requiring high performance and seamless integration with device hardware. Native development empowers developers to harness platform-specific advantages, ensuring optimal app performance and user experience.
How does Flutter compare to other cross-platform frameworks in terms of performance?
Flutter achieves competitive performance through its unique architecture that eliminates the need for a JavaScript bridge by compiling directly to native code. This approach reduces overhead and improves app responsiveness, making Flutter suitable for both UI-intensive applications and real-time data processing. However, developers should consider platform-specific optimizations and performance testing to ensure optimal app performance across different devices and operating systems. Flutter’s performance benefits from its efficient rendering engine and direct compilation to native code, enabling efficient cross platform development of high-performance apps on Android and iOS devices.
What role does Dart programming language play in Flutter app development?
Dart serves as the primary programming language for Flutter app development, offering features such as ahead-of-time (AOT) compilation and just-in-time (JIT) compilation. AOT compilation optimizes app startup time and reduces memory usage by compiling Dart code to native machine code ahead of deployment. JIT compilation, on the other hand, facilitates rapid development and debugging through its ability to compile code dynamically during app execution. Together, these features enhance developer productivity and contribute to Flutter’s efficiency in creating high-performance cross platform apps. Dart’s versatility and performance optimizations make it well-suited for building responsive and scalable apps on Android and iOS platforms.
How does Flutter support the development of desktop applications alongside mobile apps?
Flutter’s cross platform framework extends beyond mobile devices to desktop platforms, enabling developers to build native desktop applications using a single codebase. This versatility allows businesses to leverage existing Flutter expertise and resources to create applications for Windows, macOS, and Linux operating systems. Flutter’s adaptive UI components and platform-aware APIs ensure consistent user experiences across different desktop environments, facilitating seamless integration and deployment of desktop applications alongside mobile counterparts. Developers benefit from Flutter’s unified development approach, which simplifies multi-platform app development and enhances productivity across diverse operating systems.






