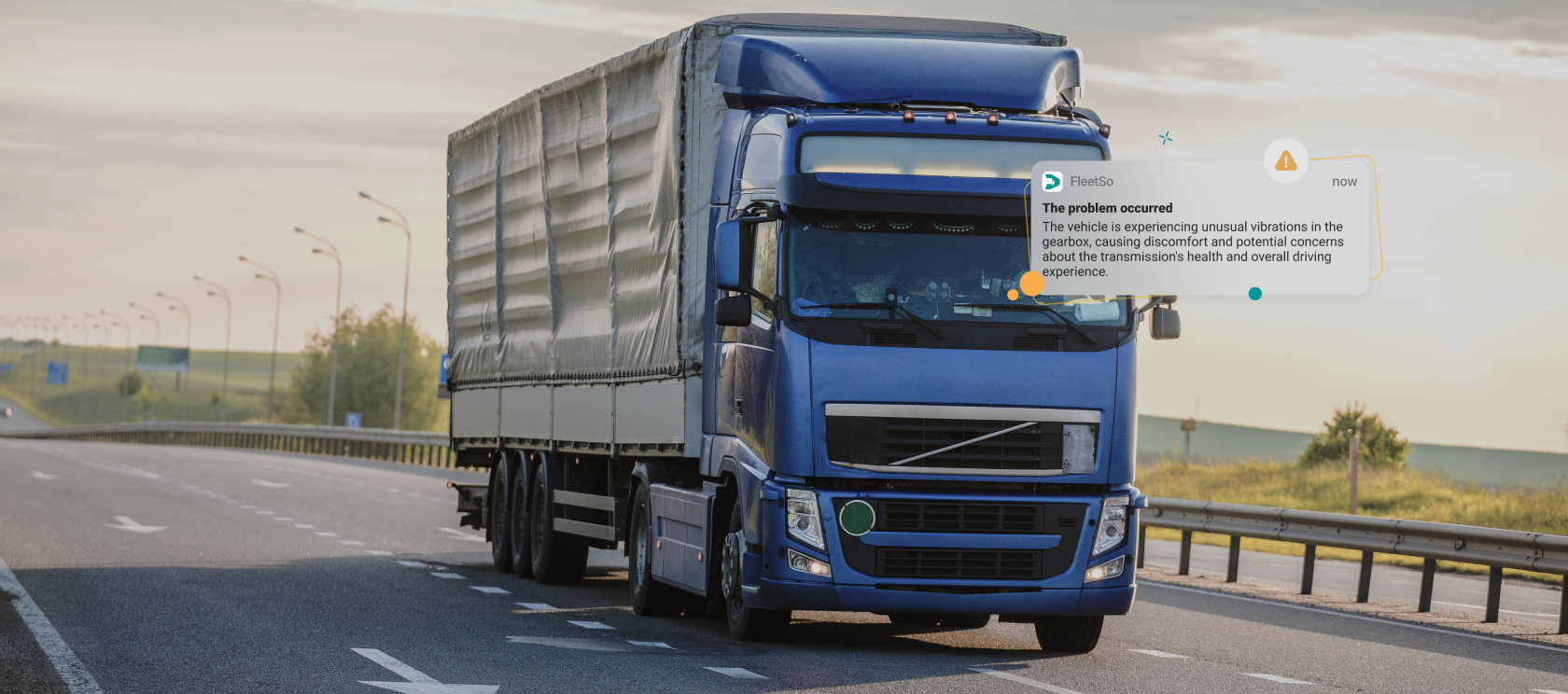
Predictive fleet maintenance has emerged as a game-changer in the world of vehicle management, revolutionizing how businesses ensure the reliability and longevity of their fleets.
As a fleet manager, these are likely some of the many challenges you face daily:
- Unscheduled downtime: Unexpected breakdowns can lead to unscheduled downtime, disrupting operations and resulting in missed deadlines or poor customer service.
- High repair costs: Emergency repairs or part replacements are often more expensive than regular maintenance, eating into the operational budget.
- Inefficient fleet utilization: Without insights into vehicle health, some vehicles may be overused while others are underutilized, leading to inefficiencies.
- Safety concerns: Breakdowns or malfunctions on the road can compromise driver safety, leading to accidents or other dangerous situations.
- Depreciating asset value: Neglected maintenance can lead to premature wear and tear, depreciating the value of fleet vehicles faster.
- Regulatory compliance: Failure to keep up with maintenance can result in non-compliance with safety and environmental regulations, potentially resulting in fines or sanctions.

However, there is a transformative solution to these issues — predictive fleet maintenance. This is a modern, data-driven approach designed to proactively identify vehicle issues before they transform into costly repairs or disruptions. It leverages cutting-edge technologies to provide actionable insights, enhancing the efficiency, safety, and longevity of your fleet. If you need a tailored solution for your operations, we offer fleet management application development to cater to your specific requirements.
And in this guide, we’ll address these frequent difficulties, offering effective strategies to overcome them. You’ll explore the differences between preventive and predictive fleet maintenance software, understand the ways predictive maintenance can boost your fleet operations, understand its working process, delve into the advanced technologies powering predictive maintenance, and discover how we can assist in implementing this solution for your fleet.
What is predictive fleet maintenance?
Predictive fleet maintenance is a proactive approach to fleet management that uses data analytics and predictive modeling to anticipate when a vehicle may require servicing.
This method employs advanced technologies like IoT sensors, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning to analyze a wide range of vehicle parameters that can indicate potential problems before they become serious. Some of these parameters include:
- Engine temperature: Overheating can be a sign of problems like coolant leaks, blocked radiators, or failing water pumps.
- Vibration levels: Increased vibration can indicate issues such as wheel alignment problems, tire imbalance, or drivetrain malfunctions.
- Oil conditions: Sensors can monitor oil level, oil temperature, and even the presence of metal fragments in the oil, which can indicate engine wear and tear.
- Battery condition: Monitoring the battery condition can prevent a sudden failure that could lead to vehicle downtime.
- Brake performance: Sensors can assess brake pad wear and tear and detect any decrease in brake fluid levels.
- Exhaust emissions: Excessive emissions can indicate engine problems or a failing catalytic converter.
The aim is to predict and prevent potential vehicle breakdowns or malfunctions, increase operational efficiency, improve safety, reduce unexpected repair costs, and enhance the lifespan of your fleet. Also, by accurately predicting when maintenance is truly needed, predictive fleet maintenance can help companies eliminate unnecessary maintenance tasks, thereby saving time and resources.
For example, a delivery company might implement predictive fleet maintenance across its large fleet of delivery vans. Each van may be equipped with IoT sensors that collect a range of data, such as engine temperature, tire pressure, fuel consumption, and driving patterns. This data is then transmitted in real-time to a centralized fleet management software system, where AI and machine learning algorithms analyze it to predict potential issues.
Should the system predict that a particular van’s engine is likely to overheat due to patterns in its coolant temperature, the company can schedule maintenance before the engine fails during a delivery route. This avoids the costs and delays associated with unexpected breakdowns and the need to replace parts, improving customer satisfaction with timely deliveries. Furthermore, this proactive approach can help extend the life of each vehicle, resulting in long-term cost savings on vehicle replacements for the company.
What is the difference between preventive and predictive fleet maintenance software?
The difference between preventive and predictive maintenance software lies in their approach to maintenance scheduling and problem detection. In a nutshell, preventive maintenance software relies on predefined schedules, while predictive maintenance software uses real-time data to predict maintenance needs.
| Preventive fleet maintenance software | Predictive fleet maintenance software | |
| Approach to maintenance scheduling | Predefined time intervals (like every six months) or usage intervals (like every 5,000 miles) | Condition-based maintenance utilizing AI and real-time data analysis |
| Maintenance task execution | Follows fixed maintenance schedule | Adjusts maintenance tasks based on actual component condition |
| Data analysis | Relies on historical maintenance data, schedules, and manufacturers’ guidelines, such as scheduled oil changes after a certain number of miles | Analyzes real-time and historical data for anomaly detection |
| Maintenance timing | Fixed intervals or predetermined time periods | Optimal timing based on real-time component condition |
| Maintenance focus | Preventive actions to avoid potential failures | Proactive actions to prevent unplanned breakdowns |
| Resource allocation | Resource planning based on scheduled maintenance | Optimized resource allocation based on real-time conditions |
| Benefits | Compliance management, standardized maintenance plans | Minimized breakdowns, optimized maintenance scheduling |
Preventive maintenance software follows manufacturers’ guidelines, like replacing the oil every 10,000 kilometers. On the other hand, predictive maintenance software uses real-time data and sophisticated algorithms to anticipate potential maintenance needs. However, it’s important to note that predictive maintenance doesn’t replace preventive maintenance. Instead, it complements it by providing a more nuanced understanding of each vehicle’s condition, helping to optimize maintenance schedules and reduce unexpected breakdowns.
Key features of preventive fleet maintenance software
Preventive maintenance software focuses on scheduled maintenance based on predetermined time or mileage intervals, regardless of the actual condition of the vehicle or its components. It follows a fixed maintenance schedule, typically based on manufacturer recommendations or industry standards. Key features of preventive maintenance software include:
- Scheduled vehicle maintenance: Maintenance tasks are planned based on predetermined intervals, such as mileage or time elapsed since the last maintenance eve
- Standardized preventative maintenance plans: Offers pre-established maintenance plans aligned with manufacturer recommendations or industry standards.
- Maintenance reminders: Automates reminders for upcoming maintenance tasks, ensuring they are not overlooked or delayed.
- Service history tracking: Maintains a record of past maintenance activities, allowing for easy reference and tracking of completed tasks.
- Compliance management: Helps ensure adherence to regulatory and warranty requirements by tracking and documenting preventative maintenance activities.
- Resource planning: Assists in resource allocation by providing visibility into upcoming preventive maintenance tasks and associated requirements.
Key features of predictive fleet maintenance software
Predictive software leverages data analysis, machine learning, and sensor data to predict when maintenance is needed. It involves monitoring the real-time condition and performance of the vehicle and its components to determine maintenance requirements. Key features of predictive maintenance software include:
- Real-time data analysis: Analyzes real-time data from vehicle sensors, telematics, and other sources to monitor vehicle health and performance.
- Anomaly detection: Identifies patterns and anomalies in the data to detect potential maintenance issues or component failures.
- Condition-based fleet predictive maintenance: Determines maintenance needs based on the actual condition of the vehicle components, rather than predetermined schedules.
- Predictive alerts: Generates proactive alerts and notifications when potential issues are detected, enabling timely intervention. Predictive maintenance occurs when AI algorithms analyze historical data to forecast potential equipment malfunctions, enabling preemptive servicing to prevent failures. Predictive maintenance software not only forecasts potential equipment malfunctions but also communicates this information in a user-friendly way. It provides comprehensive yet accessible data insights, allowing fleet managers to make informed decisions. You can read more about it in our blog post on the user experience design of fleet management apps.
- Optimal maintenance timing: Predicts the optimal timing for maintenance tasks to minimize unplanned breakdowns and optimize resource allocation.
What is more suitable for fleet maintenance: preventive or predictive fleet maintenance software?
Preventive software is effective for implementing routine maintenance and complying with manufacturer guidelines, ensuring a basic level of maintenance. However, predictive fleet management software offers more targeted and efficient maintenance, leveraging real-time data analysis to identify and address maintenance needs at the optimal time, reducing unplanned breakdowns and optimizing resource allocation. Predictive maintenance does not replace preventive maintenance, rather it enhances it.
Predictive maintenance provides a layer of intelligence, using real-time data and AI to identify potential issues before they become problems, but it does not negate the need for regular, scheduled maintenance as outlined by manufacturers’ guidelines, which preventive maintenance software helps to manage.
Keep in mind that certain maintenance tasks follow a strict schedule or external conditions and can’t necessarily be optimized with predictive maintenance.
Example 1: Oil changes
Most vehicle manufacturers recommend changing the engine oil every certain number of miles or kilometers, typically between 5,000 and 10,000. While sensors can monitor some aspects of oil health, such as temperature or pressure, they can’t determine the complete condition of the oil with current technology. The deterioration of engine oil involves complex chemical changes that sensors can’t fully capture. Therefore, following the manufacturer’s guidelines is still the best practice for oil changes.
Example 2: Seasonal tire changes
The replacement of summer tires with winter ones (and vice versa) is a maintenance task typically dictated by seasonal changes, not the condition of the vehicle itself. In most regions, this switch occurs in late spring (May) and late autumn (October). Advanced vehicle sensors or predictive maintenance algorithms can’t adjust these dates as they’re influenced by external weather conditions rather than vehicle performance data.
In these cases, preventive maintenance software that adheres to a fixed schedule proves to be invaluable. However, for many other aspects of vehicle health—like brake wear, battery condition, or engine performance—predictive maintenance can provide beneficial insights and help anticipate potential issues before they result in vehicle downtime or costly repairs.
Hence, predictive and preventive maintenance methodologies should ideally be used in tandem for comprehensive and effective fleet management. In an ideal scenario, a fleet would utilize a hybrid approach, combining both preventive and predictive maintenance software. This would ensure that while regular maintenance activities continue based on predefined schedules, the predictive system can help to identify and address issues that may not be evident during these routine checks. The combination provides a comprehensive strategy to minimize unplanned downtime, extend vehicle lifespan, and ultimately save on maintenance costs.
In this comprehensive guide on fleet management software creation, you can explore the key aspects of building a robust system for effective maintenance strategies, including preventive and predictive approaches.
Ways predictive fleet maintenance software can help your fleet operations
Using preventive analytics in fleet management can bring several benefits to the overall operations and performance of the fleet. Here are some key advantages of employing preventive analytics:
Reduced downtime
By implementing preventive analytics, fleet managers can identify potential maintenance needs before they escalate into major issues or breakdowns. Proactively addressing maintenance requirements minimizes unplanned downtime and keeps vehicles on the road, ensuring smooth operations and meeting customer commitments.
Cost savings
Preventive analytics enables fleet managers to optimize maintenance activities by replacing parts and performing maintenance tasks at the right time. This approach helps prevent costly breakdowns, reduces the need for emergency repairs, and avoids expensive component failures. Additionally, it can lead to improved fuel efficiency by ensuring vehicles are operating at their optimal performance levels. Companies utilizing predictive fleet maintenance for their truck fleets can collect data to anticipate servicing needs. This proactive approach helps them avoid expensive repairs and downtime, resulting in significantly reduced costs.
Extended vehicle lifespan
Regular maintenance based on preventive analytics helps extend the lifespan of fleet vehicles. By addressing minor issues and conducting timely inspections, fleet managers can prevent premature wear and tear and ensure vehicles remain in good working condition for a longer duration. This maximizes the return on investment in the fleet and reduces the need for frequent vehicle replacements.
Improved safety
Preventive analytics allows fleet managers to identify potential safety risks and address them proactively. By analyzing data related to vehicle conditions, driver behavior, and historical accident records, managers can take preventive measures such as training programs or addressing faulty components to enhance overall safety and minimize the risk of accidents. Incorporating predictive fleet maintenance software can greatly assist truck drivers in detecting potential issues before they escalate.
Enhanced planning and resource allocation
With preventive analytics, fleet managers gain insights into the maintenance needs of individual vehicles or the entire fleet. This information helps in the efficient planning of maintenance schedules, allocating resources appropriately, and optimizing the utilization of labor, spare parts, and maintenance facilities. It enables fleet managers to streamline operations, reduce inefficiencies, and maximize the productivity of the maintenance team.
Improved compliance
Fleet management involves adherence to various regulatory requirements, such as vehicle inspections and emissions standards. Preventive analytics can help fleet managers stay on top of compliance by providing timely reminders for inspections, maintenance tasks, and ensuring vehicles meet necessary standards. This reduces the risk of penalties, fines, or regulatory issues.
Overall, predictive fleet maintenance software helps to reduce downtime, increase cost savings, enhance safety, improve resource allocation, extend vehicle lifespan, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. It empowers fleet managers to make data-driven decisions, optimize operations, and improve the overall efficiency and performance of the fleet. Predictive fleet maintenance, combined with asset tracking at regular intervals, significantly aids in route optimization, enhancing overall business efficiency.
How does predictive fleet maintenance software work: step-by-step process
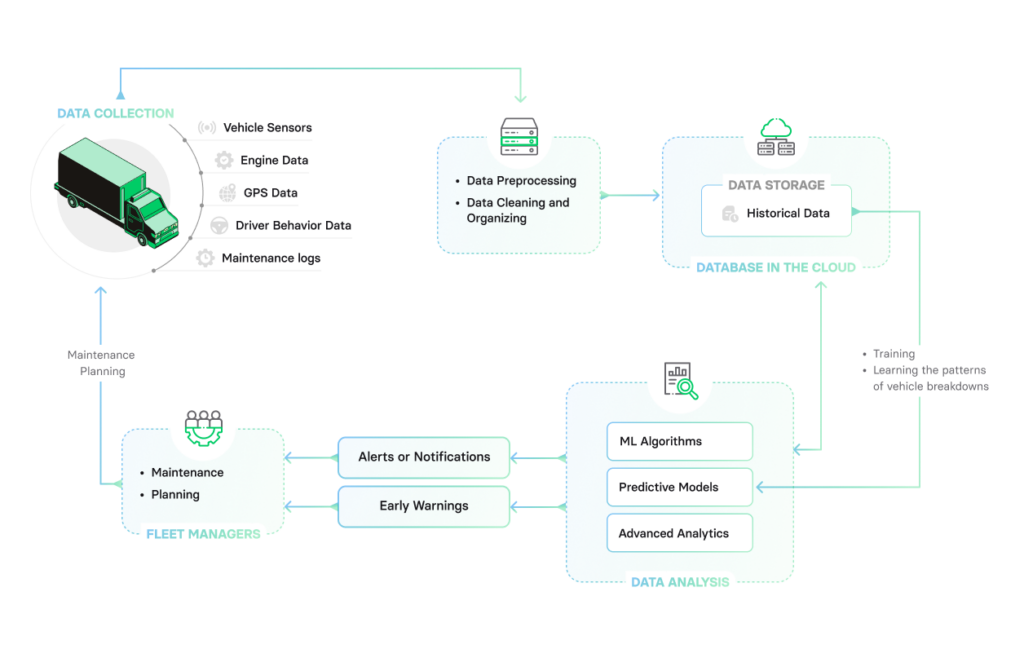
Predictive analytics for fleet maintenance works by leveraging historical and real-time data, advanced algorithms, and statistical models to forecast and anticipate maintenance needs for vehicles in a fleet. Here’s a breakdown of how it works:
Step 1: Data collection
Relevant data is collected from various sources, including telematics systems, IoT devices, maintenance records, sensor data, and other fleet management systems. This data includes information on vehicle performance, usage patterns, component health, and environmental factors.
Step 2: Data preprocessing
The collected data is cleaned, organized, and transformed into a suitable format for analysis. This involves removing outliers, addressing missing values, and normalizing the data.
Step 3: Feature selection and engineering
Relevant features or variables are selected or engineered from the data that are indicative of maintenance needs. These features could include mileage, engine temperature, fuel consumption, driver behavior, or any other relevant factors.
Step 4: Model development
Advanced analytics techniques, such as machine learning algorithms or statistical models, are employed to develop predictive models. These models learn from data patterns and relationships to make predictions about future maintenance needs.
Step 5: Model training and validation
The predictive models are trained using historical data with known maintenance outcomes. The models learn from the patterns in the data to identify correlations and make accurate predictions. The trained models are then validated using separate data to assess their performance and ensure they generalize well.
Step 6: Real-time data integration
The predictive models are integrated with real-time data feeds from the fleet vehicles. This enables the models to continuously receive and process up-to-date information about the vehicles’ condition, performance, and usage.
Step 7: Predictive maintenance alerts
Based on the real-time data and the trained models, predictive maintenance alerts are generated. These alerts notify fleet managers or maintenance personnel about specific vehicles or components that are likely to require maintenance or attention in the near future. The alerts may include details such as the recommended maintenance tasks, estimated time until maintenance, and potential risks of component failure.
Step 8: Action and decision-making
The generated alerts empower fleet managers to take proactive actions and make informed decisions regarding maintenance planning, resource allocation, and scheduling. They can prioritize maintenance tasks based on urgency, allocate resources efficiently, and minimize vehicle downtime.
Step 9: Continuous learning and improvement
Predictive maintenance models can be continuously improved by incorporating new data, monitoring the accuracy of predictions, and refining the models over time. This iterative process allows for continuous learning and enhancement of predictive capabilities.
By applying predictive analytics in fleet maintenance, fleet managers can proactively identify and address maintenance needs, minimize unplanned downtime, optimize maintenance schedules and resource allocation, reduce costs, and improve the overall efficiency and reliability of the fleet.
What advanced technologies are behind predictive fleet maintenance?
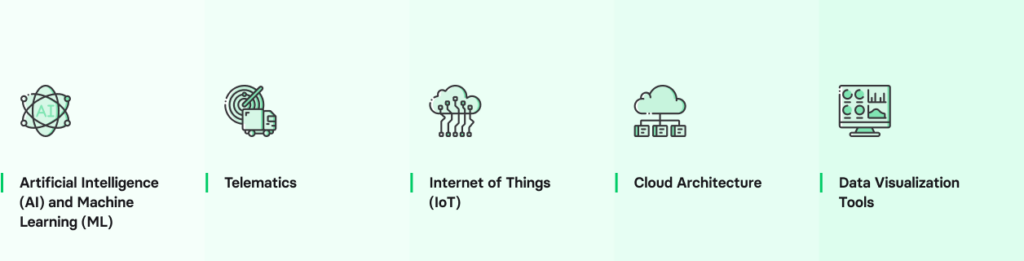
Predictive fleet maintenance leverages advanced technologies to optimize maintenance practices and prevent unexpected breakdowns. These technologies analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make accurate predictions, enabling fleet managers to take proactive measures and maximize the uptime of their vehicles. Let’s explore the key technologies that drive predictive fleet maintenance.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
By ingesting, learning from, and analyzing historical and real-time data, AI and ML can foresee potential maintenance issues before they cause operational disruption. They scrutinize a broad range of parameters – everything from engine runtime and fuel usage to driver habits and climate conditions. Here are a few practical applications of AI and ML in fleet maintenance:
- Predictive maintenance scheduling: By recognizing patterns in data, such as engine temperature and brake usage, the potential for vehicle failures can be anticipated. These predictions then facilitate the scheduling of preventative maintenance, helping to dodge breakdowns and expensive repairs.
- Fault diagnosis: By examining error codes, vehicle performance data, and maintenance history, mechanical problems can be diagnosed before leading to vehicle downtime.
- Supply chain management: Forecasting the need for spare parts becomes more accurate with the aid of data-driven predictions, helping to minimize parts shortages and maintain cost efficiency.
- Warranty management: Predictions can be made regarding which vehicles are likely to need warranty-related repairs and when. This assists fleet managers in making informed decisions about warranty purchases and renewals.
- Lifecycle analysis: By analyzing and predicting the total cost of ownership and the lifespan of each vehicle in the fleet, based on historical data and real-time performance metrics, managers can make informed decisions about when to retire or replace vehicles.
Telematics
Telematics is a technology that collects and sends information about vehicle usage and condition. It provides data that AI and ML technologies can use to make their predictions. Telematics systems use GPS and onboard diagnostics to record and map exactly where a car is and how fast it’s traveling and cross-reference this with how a car is behaving internally. This technology helps fleet managers track their vehicles, monitor their status, and understand their maintenance needs. The following are some of the ways telematics data collection is applied in fleet maintenance:
- Real-time monitoring: Telematics devices gather a vast array of data from each vehicle in real-time. This includes information about the vehicle’s location, speed, idling time, harsh braking events, fuel usage, and more. This real-time monitoring allows for immediate action if any unusual patterns are detected.
- Historical analysis: By collecting and storing data over time, telematics allows for a deep analysis of each vehicle’s history. This can highlight patterns and trends that might not be noticeable in the short term, like gradual increases in fuel consumption or subtle changes in engine performance.
- Predictive analytics: The data gathered by telematics devices can feed into AI and ML algorithms, enabling them to predict potential issues. For example, by analyzing patterns in engine temperature and oil pressure, these technologies can anticipate when an engine might be at risk of overheating.
- Operational efficiency: Telematics data can be used to identify areas where operational efficiency can be improved. This might involve analyzing fuel usage data to identify ways to reduce fuel consumption or using location data to optimize routes.
- Driver behavior analysis: Telematics can monitor driver behavior, like speed, acceleration, and braking patterns. This data can be used to identify risky driving habits and provide targeted feedback to improve driver safety and reduce wear and tear on vehicles.
Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT devices play a critical role in predictive fleet maintenance. Sensors attached to different parts of a vehicle can collect a vast amount of real-time data. This data includes engine temperature, oil levels, tire pressure, brake system health, etc. The data collected is then transmitted in real time for analysis. Analyzing data from vehicle parts via IoT sensors enables a more accurate decision making process, addressing such business problem as unexpected breakdowns. Here’s how IoT contributes to fleet maintenance:
- Real-time data collection: IoT devices, such as sensors and telematics systems, gather data on crucial vehicle parameters like engine performance, fuel consumption, tire pressure, temperature, vibration levels, and more. This real-time data provides a detailed picture of the vehicle’s health and performance.
- Remote monitoring: IoT enables fleet managers to remotely monitor the condition of their vehicles. They can access data on vehicle location, diagnostics, and performance, enabling them to detect anomalies and address potential maintenance issues promptly.
- Predictive analytics: By integrating IoT data with advanced analytics platforms, fleet managers can harness the power of predictive analytics. The continuous flow of real-time data allows for the development of accurate predictive models, helping to anticipate maintenance needs and schedule proactive repairs or replacements.
- Condition-based maintenance: IoT data enables condition-based maintenance, where maintenance activities are scheduled based on the actual condition of the vehicle rather than fixed time intervals. This approach optimizes maintenance efforts and reduces costs by focusing resources on vehicles that truly need attention.
- Fleet optimization: IoT data can be used to optimize fleet operations. For example, by analyzing vehicle performance data, fleet managers can identify inefficiencies in fuel usage, driver behavior, or routing, and take proactive steps to improve overall fleet performance and reduce maintenance needs.
- Integration with other technologies: IoT seamlessly integrates with other technologies such as AI and ML. The data collected from IoT devices can be leveraged by AI and ML algorithms to generate insights, predictions, and recommendations for more efficient and effective fleet maintenance.
Cloud architecture
Cloud architecture offers a flexible and scalable environment for managing and analyzing vast amounts of data crucial for predictive fleet maintenance. It stores and processes real-time and historical data, providing a reliable platform that can handle the extensive requirements of fleet maintenance operations. Here’s how cloud architecture is practically applied in fleet maintenance:
- Data centralization: By storing all data in one place, cloud architecture makes it easier to access and analyze information from any location. This is particularly useful for fleets that operate across multiple locations or even countries.
- Scalability: As your fleet grows, so does the amount of data you need to manage. A cloud-based system can easily scale to accommodate this growth, ensuring your fleet maintenance operations can always handle the volume of data.
- Real-time analysis: Cloud architecture supports the real-time collection and analysis of data, ensuring that the most current information is always available. This can be crucial for identifying issues and scheduling maintenance as soon as a potential problem is detected.
- Integration: Cloud systems can be easily integrated with other software tools and systems, like GPS tracking or fuel management systems. This allows all data relevant to fleet maintenance to be gathered and analyzed in one place.
- Cost-efficiency: Cloud solutions typically operate on a subscription basis, which means you only pay for the resources you use. This makes them a cost-effective solution for managing the data-heavy requirements of predictive fleet maintenance.
Data visualization tools
With all the data that predictive maintenance technologies generate, it’s important to present that data in an understandable format. Data visualization tools present complex analytical results in an easily digestible, visual format. This enables managers and decision-makers to understand the patterns and trends that predictive models uncover. Here are key ways data visualization tools help to enhance fleet maintenance:
- Visual representation: Data visualization tools convert large volumes of data into visually appealing charts, graphs, and maps, making it easier to identify patterns and trends at a glance. This visual representation allows fleet managers to quickly grasp the current state of their fleet’s health and performance.
- Real-time monitoring: These tools provide real-time monitoring of key metrics and performance indicators. Fleet managers can track vital parameters such as fuel consumption, engine health, maintenance schedules, and driver behavior, all in one centralized dashboard. Real-time monitoring helps detect anomalies and abnormalities promptly, enabling proactive decision-making.
- Customizable dashboards: Data visualization tools offer customizable dashboards, allowing fleet managers to tailor the displayed information to their specific needs. They can choose which metrics and KPIs to prioritize and arrange the visual elements according to their preferences. This flexibility ensures that the most relevant and actionable information is readily available.
- Comparative analysis: These tools enable comparative analysis by displaying data from multiple vehicles or time periods side by side. Fleet managers can compare the performance of individual vehicles, identify outliers, and spot trends across the fleet. This comparative analysis helps in identifying underperforming vehicles or areas that require improvement.
- Data exploration: Data visualization tools facilitate data exploration by providing interactive features. Fleet managers can drill down into specific data points, zoom in on time intervals, or filter data based on different criteria. This capability allows for in-depth exploration and analysis of the data, enabling better insights and decision-making.
- Communication and reporting: These tools simplify communication and reporting by providing clear and visually appealing presentations of data. Fleet managers can share reports and insights with stakeholders, highlighting key findings and performance metrics. This facilitates effective communication and supports data-driven decision-making at all levels.
How can we help to implement predictive maintenance for your fleet?
Regularly ranked among the Top Custom Software Development Companies on Clutch, Volpis has been leveraging the power of technology to help business owners achieve unparalleled efficiency. We invite you to explore our portfolio for a detailed look at the innovative software systems we have developed for our valuable clients.
At Volpis, we have a team of experts with extensive experience in implementing predictive maintenance solutions for fleets of all sizes. We understand the unique challenges faced by fleet managers and can provide tailored strategies to suit your specific needs.
If you have any questions about predictive fleet maintenance, our team would be happy to provide guidance based on your specific needs. Please don’t hesitate to reach out to us via info@volpis.com and schedule a free consultation.
Questions & Answers
FAQ
What are the disadvantages of predictive maintenance?
Predictive maintenance does have a few potential downsides. It can be expensive to set up due to the initial investment in IoT devices, software, and possibly, training for staff. It also requires a continuous flow of high-quality data, and if there are gaps or inaccuracies in this data, it may lead to erroneous predictions. Additionally, it may not be suitable for all types of maintenance tasks, some of which may still require traditional preventive measures.
What are the requirements for predictive maintenance?
Predictive maintenance requires an initial investment in hardware such as sensors or telematics systems that can collect data from vehicles. You’ll also need predictive maintenance software that can analyze this data and generate predictions. Additionally, your team might need training to understand how to interpret the data and alerts generated by the software. Finally, for optimal results, predictive maintenance requires a continuous flow of high-quality data, so maintaining the data collection systems is crucial.
How much does it cost to implement predictive maintenance in my company?
The cost of implementing predictive maintenance in fleet management largely depends on the size of your fleet, the complexity of the systems used, and the specific features of the software. It includes upfront costs for installing IoT devices like sensors and telematics systems, software development fees, and potential staff training costs.
What is predictive maintenance in fleet management?
Predictive maintenance in fleet management is a proactive approach that utilizes data analysis and technology to monitor the real-time condition and performance of vehicles. This technique helps identify potential issues before they lead to significant failures, allowing for timely repairs and maintenance.
What is predictive maintenance management?
Predictive maintenance management (PdM) involves analyzing data to detect operational irregularities and potential equipment issues, allowing for timely interventions before failures happen. This approach seeks to reduce the frequency of maintenance, prevent unplanned downtime, and cut costs associated with unnecessary preventive maintenance.
What is predictive maintenance vs CBM?
Condition-based maintenance (CBM) involves performing maintenance precisely when it is necessary, based on data collected during regular monitoring to prevent critical failures. Predictive maintenance, on the other hand, employs aggregated sensor data and analyzes trends to forecast future equipment degradation and potential failures
What is the primary goal of predictive maintenance?
The primary goal of predictive maintenance is to use data analysis to anticipate when equipment failure might occur. By monitoring asset conditions and analyzing patterns, this approach enables maintenance teams to identify potential problems before they lead to failure.
What is the difference between preventive maintenance and predictive maintenance?
The key difference between preventive and predictive maintenance lies in what triggers the maintenance activities. Preventive maintenance is done on a set schedule, such as after a certain amount of time has passed or a specific number of miles has been driven. Predictive maintenance, on the other hand, occurs as needed, based on real-time data, which indicates when a part is likely to fail or needs servicing.
What is predictive analytics?
Predictive analytics involves using data, statistical algorithms, and machine learning techniques to identify the likelihood of future outcomes based on historical data. The goal is to go beyond knowing what has happened to provide the best assessment of what will happen in the future. This approach is widely used across industries for forecasting trends, managing risks, and improving decision-making.

Kostya Khuta, the CEO of Volpis, is an expert in crafting custom software solutions for the Fleet Management, Logistics, and Transportation industry. With over 8 years of experience, he leads the way in delivering innovative and tailored solutions to meet industry-specific needs.