What is fleet compliance? In a nutshell, fleet compliance refers to policies that govern how commercial fleets are allowed to operate. True fleet compliance in the USA is when a fleet meets all of the regulations set by the Department of Transportation (DOT) and the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA).
Fleet compliance can be overwhelming. What regulations apply to your type of business? What paperwork needs to be filed with the government?
In this fleet compliance guide, we want to share some of the most important insights our team at Volpis has gathered about fleet compliance in the USA, drawing on our 8 years of experience in building customized software solutions tailored to the specific needs of various fleets.
And if you have any questions about fleet compliance or custom fleet management software development services we offer, you can always reach out to us via info@volpis.com with any concerns. We would be happy to answer all your questions and create a customized system (or add new features) for managing your vehicles and ensuring fleet compliance.
What is fleet compliance? Laws you need to comply with in the USA
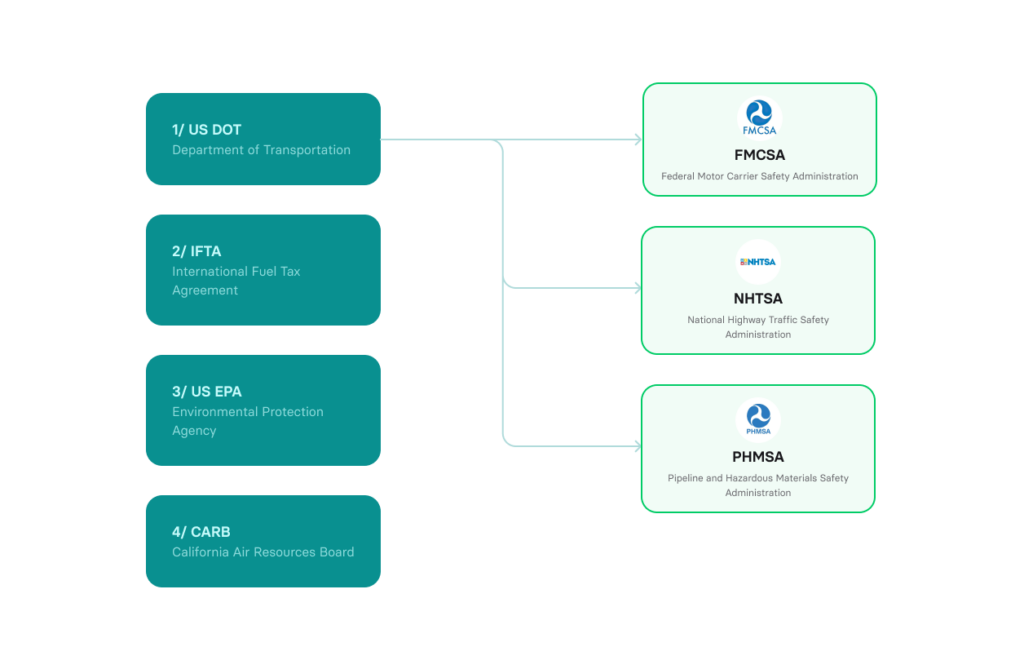
Fleet compliance involves ensuring a company’s vehicle fleet adheres to all relevant federal, state, and local regulations. In the USA, fleets need to stay compliant with the following regulations:
What is DOT?
The United States Department of Transportation (USDOT or DOT) is one of the executive departments of the U.S. federal government. You can find all current regulations of the Department of Transportation here.
The top priorities at DOT are to keep the traveling public safe and secure, increase their mobility, and have transportation systems contribute to economic growth.
What is the FMCSA?
The Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA), part of the U.S. Department of Transportation, regulates the U.S. trucking industry. For a searchable database that contains all guidance documents in effect from the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration, you can visit FMCSA’s Guidance Portal.
As the lead federal government agency responsible for regulating and providing safety oversight of commercial motor vehicles (CMVs), FMCSA’s mission is to reduce crashes, injuries, and fatalities involving large trucks and buses.
What is NHTSA?
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), a key administration within the DOT, is responsible for ensuring vehicle safety standards to reduce traffic-related injuries and fatalities.
NHTSA’s regulations cover essential areas for fleet operators, including vehicle design, crashworthiness, and safety equipment requirements.
What is PHMSA?
The Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration (PHMSA) focuses on the safe transport of hazardous materials.
Fleet operators who handle hazardous substances must comply with PHMSA’s specialized regulatory requirements. These rules cover proper labeling, packaging, and handling procedures to ensure the safety of both the public and the environment during transport.
What is IFTA?
The International Fuel Tax Agreement (IFTA) facilitates a tax distribution among 48 U.S. states and 10 Canadian provinces, enabling fleets to contribute to local fuel taxes in each area.
For IFTA reporting, it’s necessary to maintain records of trip dates (start and end), starting point and destination, stops en route, travel path, odometer readings (initial and final), total distance covered, and fuel purchases.
What is EPA?
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) enforces regulations that target emissions and environmental standards across light-duty vehicles (LDVs) and heavy-duty vehicles (HDVs) to minimize environmental impacts.
Selling an engine or vehicle in the U.S. requires proof of compliance with the Clean Air Act (CAA) and relevant EPA regulations. If the manufacturer successfully demonstrates compliance and the EPA conducts any necessary testing, the EPA can issue a Certificate of Conformity. This certificate allows for the production and sale in the U.S.
Also, The EPA SmartWay Program incentivizes fleets to implement sustainable practices. This includes the use of fuel-efficient technologies and methods to reduce idle time. Fleets that meet the EPA’s standards can receive certification.
Overview of the most important regulations: fleet compliance checklist for 2026
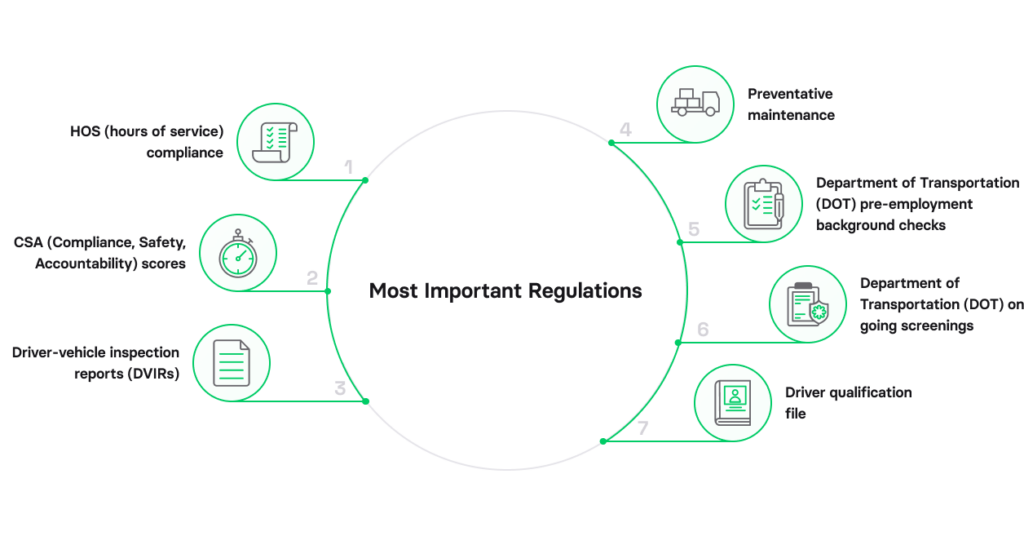
There are dozens of DOT and FMCSA regulations fleet managers need to be aware of, including safety, maintenance, federal mandates, and fuel taxes. You can find all these regulations on the official websites of FMCSA and DOT. All companies operating commercial vehicles for interstate passenger or cargo transport must register with the FMCSA and obtain a USDOT Number. This requirement applies to businesses with vehicle fleets, including delivery trucks or company cars.
In the checklist below, we included the most important aspects of fleet management affected by these regulations.
1) HOS (hours of service) compliance
The FMCSA has established HOS rules to regulate the working hours of commercial drivers, limiting how long they can drive or work without a break. These rules aim to reduce accidents caused by driver fatigue. Non-compliance with HOS rules can lead to fines, probation for carriers, and negatively impact their safety ratings.
Commercial drivers are required to use an Electronic Logging Device (ELD) for HOS tracking. These devices automatically record driving time by connecting to the vehicle’s engine, providing a dependable way to gather HOS data. To ensure HOS compliance, fleets must:
- Keep HOS Record of Duty Status (RODS) logs for six months.
- Identify and rectify missing logs for a complete retention history.
- Accurately document any log discrepancies.
- Promptly review received logs for correct application.
- Monitor logs for any rule violations and ensure event annotations are precise.
2) CSA (Compliance, Safety, Accountability) scores
CSA stands for Compliance, Safety, Accountability. CSA is the FMCSA’s safety compliance and enforcement initiative. Through the CSA’s Safety Management System (SMS), drivers receive a BASIC (Behavior Analysis and Safety Improvement Category) score from seven criteria, which remains with them indefinitely. The BASIC score evaluates:
- Crash indicator: Records of vehicle accidents, their frequency, and impact.
- Controlled substances/alcohol: Occasions of driving under the influence of alcohol or prohibited substances.
- Driver fitness: Instances of driving without a valid commercial license or medical certification, or lack of qualifications.
- Hazardous materials compliance: Situations of improper handling, labeling, or transportation of hazardous materials.
- HOS compliance: Failure to keep duty status records or violating hours of service (HOS) driving limits.
- Unsafe driving: Incidents of not using seatbelts, speeding, or engaging in risky driving actions such as harsh braking.
- Vehicle maintenance: Cases of not conducting cargo, neglecting brake, light, and system repairs, or attempting to cut maintenance costs.
3) Driver-vehicle inspection reports (DVIRs)
Pre- and post-trip inspections, known as Driver-Vehicle Inspection Reports (DVIRs), confirm the vehicle is fit to be on the road and mitigate risks for drivers and the public. The DVIR process encompasses:
- Pre-trip inspection: A required comprehensive check of the vehicle and its parts, including a review of the last DVIR. It’s mandatory before each journey and daily on trips extending over one day.
- Post-trip inspection: This inspection must be done after every workday. A distinct DVIR is necessary for each vehicle used. All problems must be documented and reported for repair.
- Defect report: Post-inspection, any defects affecting vehicle safety must be logged and communicated.
- Corrective action: After repairs, drivers must confirm by signing that corrections were made promptly.
- Possible exemptions: Exemptions to DVIRs may apply to specific categories such as driver-towaway operations, private passenger carriers, and operators of a single CMV.
A standard DVIR inspection should include the following: date; vehicle; identification; driver identification; steering; wheels, tires, and rims; brakes; air systems; lights and reflectors; mirrors; fire extinguishers, first-aid kits, and other safety equipment; windshield wipers; coupling equipment and fifth wheels; power units and trailer.
4) Preventative maintenance
Preventative maintenance is essential for safety and compliance with DOT regulations. Depending on the vehicle’s specifics, a preventative maintenance checklist might include:
- Oil and filter replacements
- Engine tune-ups, including belts and fluids
- Brake checks
- Tire servicing and alignment
- Lubrication
- Cooling system upkeep
- Electrical systems maintenance
- Window integrity
- Instrument panel checks
- Battery maintenance
- Transmission care
- Rust and corrosion management
5) Department of Transportation (DOT) pre-employment background checks
Pre-employment (background) checks, mandated by the DOT, are critical for verifying the qualifications of commercial motor vehicle drivers. To meet DOT compliance, companies under DOT regulation must perform these checks during the recruitment phase. The checks required by the DOT cover:
- Driving records
- Verification of DOT employment history
- FMCSA drug and alcohol history screen
- DOT pre-employment drug test
- DOT physical examination
6) Department of Transportation (DOT) on-going screenings
Employment screenings extend beyond the hiring stage. Regular monitoring of drug and alcohol use, driving records, and criminal backgrounds is crucial. DOT regulations for drug and alcohol testing encompass:
- An assigned contact in your company.
- Screenings for drivers, dispatchers, maintenance workers, volunteers, and security personnel.
- Strict bans on substances like marijuana, cocaine, amphetamines, opiates, and phencyclidine.
- A prohibition on alcohol consumption four hours before work or during on-call periods.
- Random testing must comply with DOT’s selection criteria.
- Tests based on reasonable suspicion.
- Post-accident testing.
7) Driver qualification file
Driver qualification file gathers documents proving a driver’s capability to drive a commercial motor vehicle (CMV). The law mandates DQ files for CMV drivers, including those operating vehicles over 10,000 pounds, passenger vehicles carrying 8 or more people, and vehicles transporting hazardous materials. Driver qualification files should include the following items:
- Job application
- Driving history report
- CDL and road test certification
- Record of violations
- Yearly evaluations
- Health documentation
- Medical clearance paperwork
- Drug and alcohol screening outcomes
- Vehicle inspection reports for defects
- Logbooks and auxiliary records
- Vehicle upkeep and repair logs
How to stay compliant in fleet operations: fleet compliance best practices
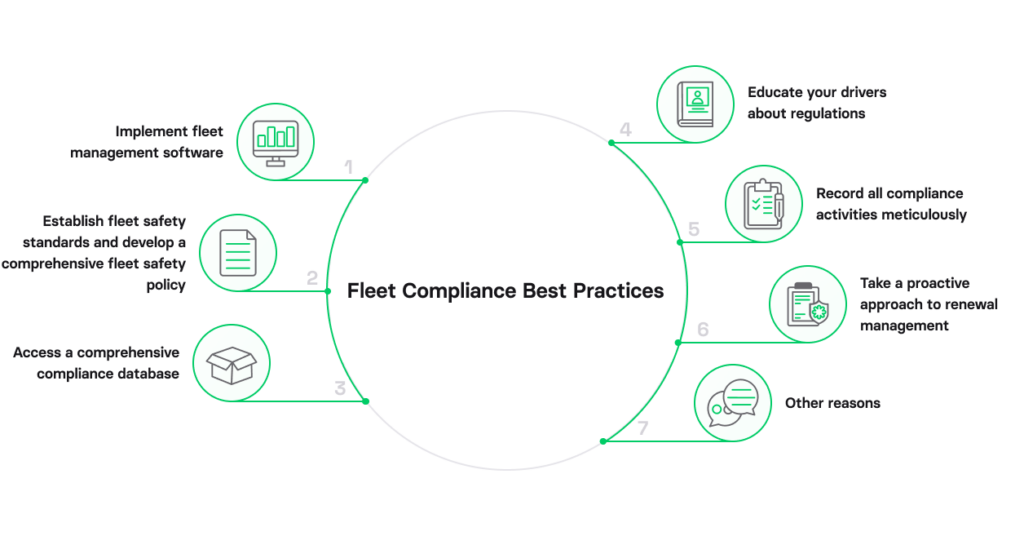
Navigating the complexities of fleet compliance demands more than just adherence to regulations. It’s all about strategically employing industry best practices and innovative tools to ensure your fleet operates smoothly.
Implement fleet management software
Understanding the need to comply with regulations is one thing; going beyond mere compliance through strategic use of technology is what can keep your fleet ahead. Implementing fleet management software can help your company stay compliant and avoid costly penalties.
Establish fleet safety standards and develop a comprehensive fleet safety policy
Implementing safety procedures is crucial to promoting fleet safety and maintaining compliance. Tailor safety standards to suit your fleet’s requirements, considering the operation of various vehicles. A robust fleet safety policy outlining expectations for employee behavior, such as mandatory seatbelt use, speed limit adherence, and zero tolerance for impaired driving, is essential. Employees must understand the consequences of not following the safety policy, which can include losing their driving privileges or termination.
Access a comprehensive compliance database
Fleet managers need access to a comprehensive database outlining compliance best practices. This access enables them to effectively evaluate and control the risks tied to their fleet operations. Moreover, leveraging this data can enhance the efficiency of fleet management processes.
Educate your drivers about regulations
Continuously provide them with training and coaching on compliance. It’s crucial to have a system in place for monitoring safe driving practices to ensure accountability. This enables you to recognize and reward drivers with exemplary records while addressing risky behaviors promptly.
Record all compliance activities meticulously
This detailed documentation will provide the necessary data to navigate regulatory audits or inspections, helping to prevent penalties and fines. Additionally, you can leverage insights gleaned from this data to enhance fleet performance.
Take a proactive approach to renewal management
This involves staying on top of deadlines and acting before they lapse. It’s important to ensure you have a robust system in place to track compliance-related data, including vehicle registrations and driver’s license renewals.
Track your vehicles throughout their life cycle as your fleet expands
From acquisition and maintenance to disposition and replacement, maintaining a solid tracking system is crucial. A robust fleet compliance program ensures your vehicles are well-maintained and safe for operation.
Conduct electronic driver vehicle inspection reports
Perform Electronic Driver Vehicle Inspection Reports (eDVIRs) to comply with FMCSA regulation 396.11, requiring commercial motor carriers to complete and maintain records of DVIRs. Conducting daily DVIRs ensures compliance, while routine inspections offer valuable insights into vehicle conditions. Many fleet managers opt for eDVIRs with driver inspection apps to maintain comprehensive compliance records and utilize inspection results for maintenance. Drivers can easily complete thorough eDVIRs in a mobile fleet app, eliminating the need for messy paperwork during roadside checks and DOT audits. This accessible, complete history of inspection data on their mobile devices serves as proof of fleet compliance.
Utilize inspection findings to conduct maintenance procedures
Regular vehicle inspections empower your drivers to detect any potential issues that might lead to downtime or accidents. Respond promptly to address these issues by scheduling maintenance to mitigate potential downtime or further complications. Swift resolution of maintenance concerns ensures vehicle safety and helps drivers steer clear of violations and fines.
Stick to preventive maintenance schedules
Proactive maintenance measures can keep your fleet running smoothly and prevent unexpected issues. Establishing maintenance schedules and a fleet maintenance checklist guarantees routine servicing, enhancing safety and extending vehicle lifespan. Adherence to a preventive maintenance program ensures compliance, meets warranty standards, and maintains safe operation.
Monitor driver behavior
Encourage safe driving practices among your drivers to prioritize fleet safety. Establish clear procedures for managing driver behavior. Emphasize to your drivers the importance of adhering to safety regulations to ensure compliance and avoid penalties. Leveraging GPS and telematics technologies can be immensely helpful in tracking drivers’ routes and identifying risky driving behaviors like abrupt braking or exceeding speed limits. By providing real-time data, actionable insights, and customized training modules, fleet management software can be instrumental in fostering a culture of safety among your drivers.
What is a fleet compliance management system?

A fleet compliance management system is a robust software solution aimed at ensuring a company’s fleet and drivers comply with diverse regulatory and safety standards. These systems facilitate monitoring and maintaining compliance across various requirements, including vehicle inspections, driver certifications, hours of service regulations, emissions standards, and more. They often come with features like:
- Comprehensive regulatory and safety compliance: ensures adherence to diverse regulatory and safety standards governing fleet operations.
- Documentation management: centralizes documentation management for easy access to compliance-related records and audits.
- Monitoring of compliance: facilitates continuous monitoring across various requirements.
- Vehicle inspections: streamlines the process of conducting and documenting vehicle inspections as per regulatory guidelines.
- Maintenance scheduling: automates maintenance scheduling to ensure timely servicing and repairs, reducing downtime.
- Driver certifications: manages driver certifications and qualifications, ensuring they meet regulatory standards.
- Hours of service regulations: tracks and enforces compliance with hours of service regulations to prevent driver fatigue and ensure road safety.
- Emissions standards: monitors vehicle emissions to comply with environmental regulations and reduce environmental impact.
- Real-time tracking: provides real-time tracking of fleet vehicles for enhanced visibility and monitoring.
- Automated reporting: generates automated reports on compliance status, violations, and corrective actions.
Benefits of using fleet management software to maintain compliance
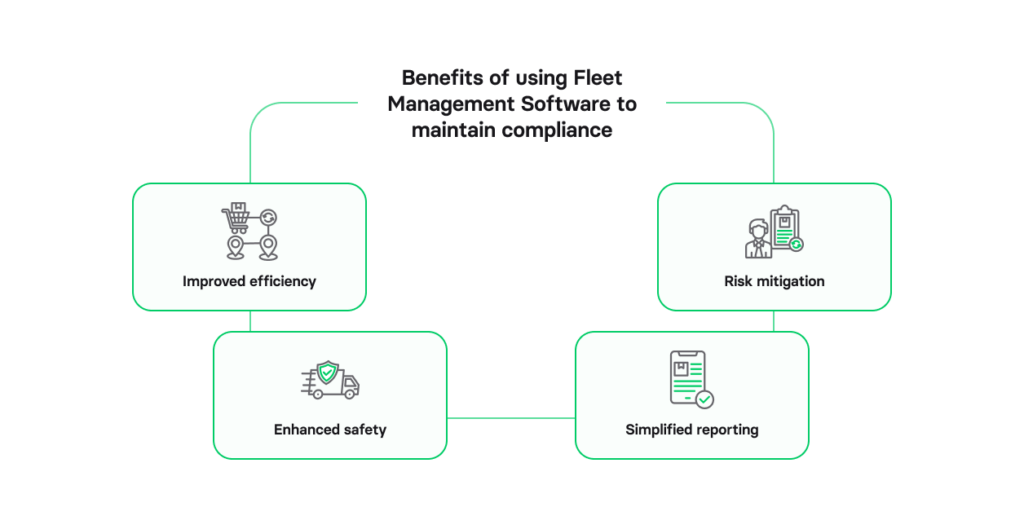
Integration of fleet management systems provides comprehensive visibility into your entire fleet. This facilitates a more compliance-proof maintenance process:
- Improved efficiency
Compliance management systems automate manual processes, boosting efficiency, reducing administrative tasks, and enhancing productivity.
- Risk mitigation
Centralizing compliance data and automating checks help identify and address issues promptly, minimizing the risk of fines, penalties, and accidents.
- Enhanced safety
Such systems monitor driver behavior and vehicle maintenance, lowering accident rates and fostering a safer work environment.
- Simplified reporting
Fleet management systems streamline compliance reporting, improving regulatory adherence and providing valuable insights for continuous improvement.
Centralizing all documentation in an easily accessible location can greatly facilitate audits and help avoid hefty fines. Fleet management software streamlines the inspection process by digitizing it. Also, it stores all inspection data within the app, ensuring easy access whenever needed.
Factors to consider when selecting fleet compliance management system
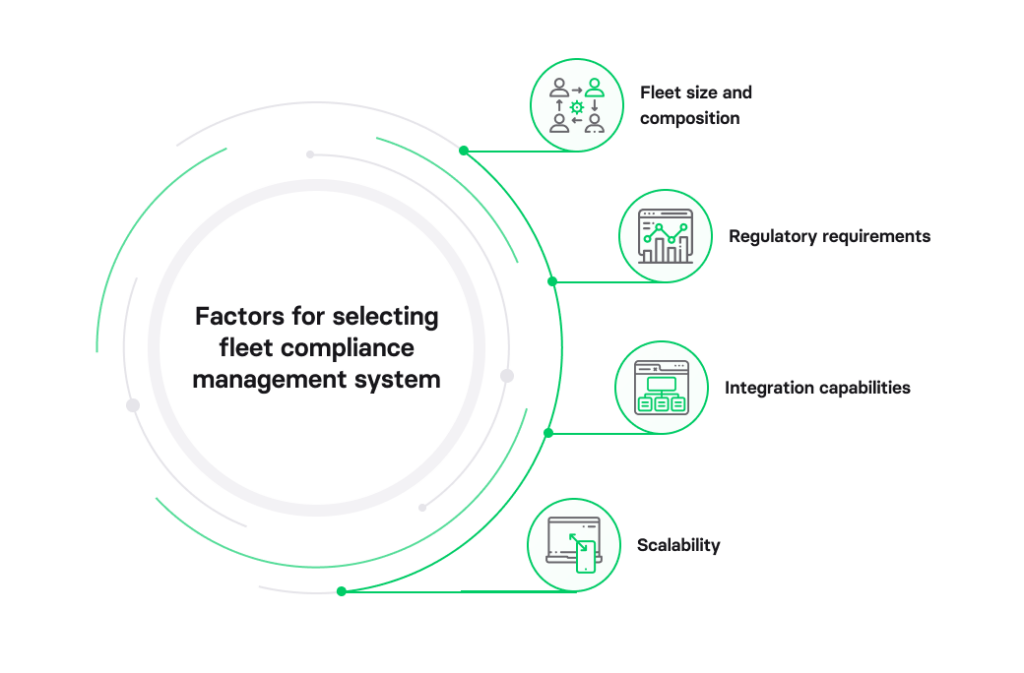
Selecting the optimal fleet compliance management system involves evaluating several key factors:
Factor 1: Fleet size and composition
The size and makeup of your fleet directly influence your compliance management requirements. While smaller fleets may need simpler solutions, larger and more diverse fleets demand robust systems.
Factor 2: Regulatory requirements
Compliance regulations vary across industries and regions. Ensure that the system you select can adapt to the specific regulations governing your operations.
Factor 3: Integration capabilities
The system’s ability to integrate with other software and hardware solutions in your organization is critical. Compatibility with existing systems like GPS tracking or maintenance software can streamline processes.
Factor 4: Scalability
Consider the scalability of the system. As your fleet grows and evolves, you’ll need a solution that can effortlessly grow with you. Investing in a scalable system ensures long-term efficiency and cost savings.
What are the best software options for ensuring compliance and managing fleets?
The software tools below offer powerful ways to help manage your fleet compliance.
Fleetsu

Developed by our experts at Volpis for our customer, Fleetsu is a tailored fleet management application that offers real-time GPS vehicle tracking, vehicle diagnostics, driver behavior monitoring, and more. It boasts an intuitive user interface and customizable dashboards, empowering managers to closely monitor their fleet and make well-informed decisions.
Fleetio

Fleetio is a cloud-based software that equips businesses with tools for vehicle management, maintenance scheduling, fuel consumption tracking, and more. It offers features such as real-time fleet tracking, automated maintenance schedules, and customizable reporting.
Onfleet

Onfleet specializes in delivery management, assisting businesses in optimizing their last-mile delivery operations. It provides functionalities like real-time tracking, driver dispatching, and customer notifications.
Samsara

Known for its driver rewards programs, Samsara makes it easier to encourage safe and efficient driving within your team. Plus, it’s packed with features to cut costs and keep your fleet running smoothly.
Azuga

Azuga shines with its integration with fuel cards, pointing your drivers to the cheapest gas stations around. It also offers discounts on maintenance and tires at select locations.
Motive

Motive lets your drivers take an active part in keeping up with maintenance. They get alerts for fuel checks and can report vehicle damage right away.
How we build tailor-made software to help companies ensure fleet compliance
Regularly ranked among the Top Custom Software Development Companies on Clutch.co, Volpis has been leveraging the power of technology to assist business owners in maintaining fleet compliance.
We invite you to explore our portfolio for a detailed look at the innovative software solutions we have developed for our valuable clients.
Read more reviews from our valuable customers here
If you have any questions or need further information about maintaining fleet compliance or our software development services, please do not hesitate to contact us at info@volpis.com
Questions & Answers
FAQ
What are fleet regulations?
Fleet regulations refer to the set of laws and guidelines governing the operation, safety, and compliance of commercial fleets. These regulations encompass various aspects such as vehicle maintenance, driver qualifications, and transportation standards.
What is fleet compliance?
Fleet compliance entails adhering to regulatory requirements and industry standards to ensure the legality, safety, and efficiency of fleet operations. It involves implementing practices and systems to meet legal obligations and mitigate risks associated with fleet management.
What are fleet management standards?
Fleet management standards are established guidelines and protocols for efficiently managing a fleet of vehicles. These standards cover areas such as vehicle maintenance, driver training, fuel management, and safety procedures to optimize fleet performance and ensure regulatory compliance.
What are the steps of fleet management?
Fleet management typically involves several steps, including vehicle acquisition, maintenance scheduling, driver training, route optimization, and performance monitoring. By systematically managing these aspects, fleet managers can maximize operational efficiency and ensure regulatory compliance.
How do fleet management systems work?
Fleet management systems utilize technology such as GPS tracking, telematics, and data analytics to monitor vehicle location, performance, and driver behavior in real-time. These systems provide fleet managers with valuable insights and tools to optimize fleet operations and ensure compliance.
What are the 5 elements of effective fleet management?
Effective fleet management typically comprises five key elements: vehicle acquisition and disposal, maintenance management, fuel management, driver management, and compliance with regulations. Balancing these elements ensures the smooth functioning of the fleet while meeting organizational objectives.
What do fleet managers need to know?
Fleet managers need to have comprehensive knowledge of regulations, vehicle maintenance practices, driver safety protocols, and industry trends. They must also be adept at utilizing technology and data analysis tools to optimize fleet performance and ensure compliance.
What is fleet safety?
Fleet safety involves implementing policies, procedures, and training programs to minimize the risk of accidents, injuries, and property damage within a fleet. It encompasses measures such as driver training, vehicle maintenance, and compliance with safety regulations to ensure the well-being of drivers and the public.
What is fleet reporting?
Fleet reporting involves generating and analyzing data related to fleet operations, including vehicle usage, maintenance, fuel consumption, and compliance metrics. These reports provide valuable insights for fleet managers to make informed decisions, improve efficiency, and ensure regulatory compliance.
What is regulated by the DOT?
The Department of Transportation (DOT) regulates various aspects of transportation, including vehicle safety standards, driver qualifications, hours of service regulations, and hazardous materials transportation. Compliance with DOT regulations is mandatory for commercial carriers operating within the United States.
What is DOT compliance?
DOT compliance refers to adhering to the regulations set forth by the Department of Transportation to ensure the safety, efficiency, and legality of commercial transportation operations. It encompasses various requirements related to vehicle inspections, driver qualifications, and hours of service limits.
What is the definition of on-duty for DOT regulations?
In DOT regulations, being “on-duty” refers to the time when a commercial driver is performing work-related tasks, including driving, loading/unloading cargo, inspecting vehicles, and completing paperwork. On-duty time is subject to regulations governing maximum hours of service to prevent driver fatigue and ensure safety on the road.
What penalties can fleet managers face for failing to comply with fleet management regulations?
The consequences for non-compliance vary based on the severity and nature of the violations. Regulatory bodies have the authority to impose fines ranging from hundreds to thousands of dollars per infraction. In severe cases, they may even suspend a fleet’s operating license.






